Three Decades of Advances in Arabinogalactan-Protein Biosynthesis
- PMID: 33384708
- PMCID: PMC7769824
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2020.610377
Three Decades of Advances in Arabinogalactan-Protein Biosynthesis
Abstract
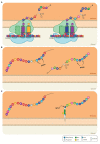
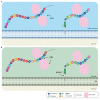
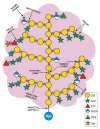
Arabinogalactan-proteins (AGPs) are a large, complex, and highly diverse class of heavily glycosylated proteins that belong to the family of cell wall hydroxyproline-rich glycoproteins. Approximately 90% of the molecules consist of arabinogalactan polysaccharides, which are composed of arabinose and galactose as major sugars and minor sugars such as glucuronic acid, fucose, and rhamnose. About half of the AGP family members contain a glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI) lipid anchor, which allows for an association with the outer leaflet of the plasma membrane. The mysterious AGP family has captivated the attention of plant biologists for several decades. This diverse family of glycoproteins is widely distributed in the plant kingdom, including many algae, where they play fundamental roles in growth and development processes. The journey of AGP biosynthesis begins with the assembly of amino acids into peptide chains of proteins. An N-terminal signal peptide directs AGPs toward the endoplasmic reticulum, where proline hydroxylation occurs and a GPI anchor may be added. GPI-anchored AGPs, as well as unanchored AGPs, are then transferred to the Golgi apparatus, where extensive glycosylation occurs by the action of a variety glycosyltransferase enzymes. Following glycosylation, AGPs are transported by secretory vesicles to the cell wall or to the extracellular face of the plasma membrane (in the case of GPI-anchored AGPs). GPI-anchored proteins can be released from the plasma membrane into the cell wall by phospholipases. In this review, we present an overview of the accumulated knowledge on AGP biosynthesis over the past three decades. Particular emphasis is placed on the glycosylation of AGPs as the sugar moiety is essential to their function. Recent genetics and genomics approaches have significantly contributed to a broader knowledge of AGP biosynthesis. However, many questions remain to be elucidated in the decades ahead.
Keywords: arabinogalactan-proteins, arabinogalactan-proteinbiosynthesis; cell wall; glycosylation; glycosyltransferases; glypiation; hydroxyproline; proline hydroxylation.
Copyright © 2020 Silva, Ferraz, Dupree, Showalter and Coimbra.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Back to the future with the AGP-Ca2+ flux capacitor.Ann Bot. 2014 Oct;114(6):1069-85. doi: 10.1093/aob/mcu161. Epub 2014 Aug 19. Ann Bot. 2014. PMID: 25139429 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Arabinogalactan proteins - Multifunctional glycoproteins of the plant cell wall.Cell Surf. 2023 Feb 17;9:100102. doi: 10.1016/j.tcsw.2023.100102. eCollection 2023 Dec. Cell Surf. 2023. PMID: 36873729 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extensin and Arabinogalactan-Protein Biosynthesis: Glycosyltransferases, Research Challenges, and Biosensors.Front Plant Sci. 2016 Jun 15;7:814. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2016.00814. eCollection 2016. Front Plant Sci. 2016. PMID: 27379116 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biochemical and physiological characterization of fut4 and fut6 mutants defective in arabinogalactan-protein fucosylation in Arabidopsis.J Exp Bot. 2013 Dec;64(18):5537-51. doi: 10.1093/jxb/ert321. Epub 2013 Oct 14. J Exp Bot. 2013. PMID: 24127514 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Arabinogalactan Type II Degradation in Plant-Microbe Interactions.Front Microbiol. 2021 Aug 25;12:730543. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.730543. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34512607 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Arabinogalactan Proteins in Plant Roots - An Update on Possible Functions.Front Plant Sci. 2021 May 17;12:674010. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.674010. eCollection 2021. Front Plant Sci. 2021. PMID: 34079573 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Life cycle and functional genomics of the unicellular red alga Galdieria for elucidating algal and plant evolution and industrial use.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022 Oct 11;119(41):e2210665119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2210665119. Epub 2022 Oct 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022. PMID: 36194630 Free PMC article.
-
OsFLA1 encodes a fasciclin-like arabinogalactan protein and affects pollen exine development in rice.Theor Appl Genet. 2022 Apr;135(4):1247-1262. doi: 10.1007/s00122-021-04028-1. Epub 2022 Jan 5. Theor Appl Genet. 2022. PMID: 34985538
-
Ovary Signals for Pollen Tube Guidance in Chalazogamous Mangifera indica L.Front Plant Sci. 2021 Feb 10;11:601706. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2020.601706. eCollection 2020. Front Plant Sci. 2021. PMID: 33643328 Free PMC article.
-
Biochemical and Functional Characterization of GALT8, an Arabidopsis GT31 β-(1,3)-Galactosyltransferase That Influences Seedling Development.Front Plant Sci. 2021 May 25;12:678564. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.678564. eCollection 2021. Front Plant Sci. 2021. PMID: 34113372 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

