Effect of Nd: YAG laser irradiation to the temporomandibular joint on taste threshold
- PMID: 33384806
- PMCID: PMC7770286
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jds.2020.05.016
Effect of Nd: YAG laser irradiation to the temporomandibular joint on taste threshold
Abstract
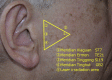
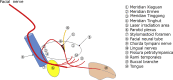
Background/purpose: The tissue absorption laser has been clinically applied to alleviate pain in various areas. It is used for pain relief from temporomandibular disease (TMD) in dentistry. Although the facial and trigeminal nerves are distributed around the temporomandibular joint, the effects of laser irradiation and absorption on the neural functions have not been directly studied. In this study, the Nd:YAG laser was applied to an area where the facial nerve passes with photonic radiation for the treatment of TMD.
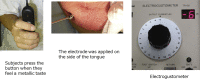
Materials and methods: Ten volunteers including seven males and three females were selected as subjects. Nd:YAG laser was irradiated area included several internal and external standard and associated acupuncture points. The chorda tympani nerve, a branch of facial nerve is distributed to the front two thirds of the tongue and is associated with the sense of taste. We evaluated the effect of laser irradiation and absorption on the taste function by means of an electric taste meter.
Results: No significant difference was identified in the values between before and after laser irradiation (Wilcoxon signed-rank test).
Conclusion: It was confirmed that there was no effect on taste function while applying Nd:YAG laser irradiation around the TMD joint.
Keywords: Acupuncture point; Electric taste meter; Nd:YAG laser irradiation; Taste threshold; Temporomandibular joint; The chorda tympani nerve.
© 2020 Association for Dental Sciences of the Republic of China. Publishing services by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose relates to this study.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Nd:YAG laser irradiation of the human dental pulp: implications as a predictor of pulp hemodynamics.Lasers Surg Med. 2000;26(3):270-6. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1096-9101(2000)26:3<270::aid-lsm4>3.0.co;2-9. Lasers Surg Med. 2000. PMID: 10738289
-
Clinical effectiveness of laser acupuncture in the treatment of temporomandibular joint disorder.J Formos Med Assoc. 2014 Aug;113(8):535-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jfma.2012.07.039. Epub 2012 Aug 29. J Formos Med Assoc. 2014. PMID: 25037758
-
The effects of Er:YAG, Nd:YAG, and Diode (940nm) Lasers irradiation on Microtensile bond strength of two steps self-etch adhesives.Laser Ther. 2019 Jun 30;28(2):131-137. doi: 10.5978/islsm.19-OR-10. Laser Ther. 2019. PMID: 32921912 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence of chorda tympani dysfunction in patients with burning mouth syndrome.J Am Dent Assoc. 2007 May;138(5):628-33. doi: 10.14219/jada.archive.2007.0234. J Am Dent Assoc. 2007. PMID: 17473041
-
[Rabbit facial nerve damager after Nd: YAG laser irradiation: an experimental study].Shanghai Kou Qiang Yi Xue. 1999 Dec;8(4):197-9. Shanghai Kou Qiang Yi Xue. 1999. PMID: 15048207 Chinese.
Cited by
-
Efficacy of knee osteoarthritis by use of laser acupuncture: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Jun 21;103(25):e38325. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000038325. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 38905420 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Goncalves D.A., Dal Fabbro A.L., Campos J.A., Bigal M.E., Specialist J.G. Symptoms of temporomandibular disorders in the population: an epidemiological study. J Orofac Pain. 2010;24:270–278. - PubMed
-
- Olrando B., Manfredin iD., Boso M. Efficacy of physical therapy in the treatment of Masticatory myofascial pain: a literature reviews. Minerva Stomatol. 2006;55:355–366. - PubMed
-
- Okeson J.P. Epidemiology of temporomandibular disorders. In: Okeson J.P., editor. Orofacial pain. Guide line for assessment, diagnosis, and management. Quintessence Publishing; Tokyo: 1996. p. 117.
-
- Sarlani E. Diagnosis and treatment of orofacial pain. Braz J Oral Sci. 2003;2:283–290.
-
- Albertin A., Kerppers, Amorim C.F., Costa R.V., Ferrari Correa J.C., Oliveira C.S. The effect of manual therapy on masseter muscle pain and spasm. Electromyogr Clin Neurophysiol. 2010;50:107–112. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources