Glypican-3: A molecular marker for the detection and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma☆
- PMID: 33384879
- PMCID: PMC7771890
- DOI: 10.1016/j.livres.2020.11.003
Glypican-3: A molecular marker for the detection and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma☆
Abstract
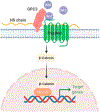
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a malignant tumor with a fairly poor prognosis (5-year survival of less than 50%). Using sorafenib, the only food and drug administration (FDA)-approved drug, HCC cannot be effectively treated; it can only be controlled at most for a couple of months. There is a great need to develop efficacious treatment against this debilitating disease. Glypican-3 (GPC3), a member of the glypican family that attaches to the cell surface by a glycosylphosphatidylinositol anchor, is overexpressed in HCC cases and is elevated in the serum of a large proportion of patients with HCC. GPC3 expression contributes to HCC growth and metastasis. Furthermore, several different types of antibodies targeting GPC3 have been developed. The aim of this review is to summarize the current literatures on the GPC3 expression in human HCC, molecular mechanisms of GPC3 regulation and antibodies targeting GPC3.
Keywords: Glypican-3 (GPC3); Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC); Wnt signaling.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Wide-ranging online data for epidemiologic research (WONDER). Underlying cause of death output based on the Detailed Mortality File. https://wonder.cdc.gov/. Accessed Aug 2, 2020.
-
- Villanueva A Hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2019;380:1450–1462. - PubMed
-
- Ronot M, Bouattour M, Wassermann J, et al. Alternative Response Criteria (Choi, European association for the study of the liver, and modified Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors [RECIST]) versus RECIST 1.1 in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma treated with sorafenib. Oncologist. 2014;19:394–402. - PMC - PubMed
