The p53 signaling pathway of the large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea) responds to acute cold stress: evidence via spatiotemporal expression analysis of p53, p21, MDM2, IGF-1, Gadd45, Fas, and Akt
- PMID: 33384900
- PMCID: PMC7751413
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.10532
The p53 signaling pathway of the large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea) responds to acute cold stress: evidence via spatiotemporal expression analysis of p53, p21, MDM2, IGF-1, Gadd45, Fas, and Akt
Abstract
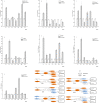
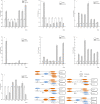
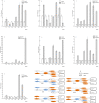
The p53 activation is induced by stressors, such as DNA damage, oxidative stress, and activated oncogenes, and can promote cell cycle arrest, cellular senescence, and apoptosis. The large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea) is an important warm temperate marine fish in the Chinese aquiculture industry. However, few studies have investigated the role of p53 in the response of L. crocea to environmental stressors. Therefore, the aim of the present study was to assess the spatiotemporal mRNA expression levels of genes involved in the p53 signaling pathway of the large yellow croaker in response to cold stress. The results showed significant changes in the expression levels of p53, p21, MDM2, IGF-1, Gadd45, Fas, and Akt in various tissues of the large yellow croaker in response to cold stress for different times. As compared to the control group, p53 mRNA expression was upregulated in most of the examined tissues at 24 h with the exception of the gill. In the liver, the expression levels of p53 and Fas were significantly decreased at 12 h, while those of p21, MDM2, IGF-1, Gadd45 were dramatically increased. Akt expression was notably changed in response to cold in several tissues. These results suggested that p53 was potentially a key gene in the large yellow croaker response to cold and possibly other environmental stressors.
Keywords: Cold stress; Gene network; Large yellow croaker; mRNA expression; p53 signaling pathway.
©2020 Qian et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare there are no competing interests.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Genome-Wide Identification of Hsp70 Genes in the Large Yellow Croaker (Larimichthys crocea) and Their Regulated Expression Under Cold and Heat Stress.Genes (Basel). 2018 Nov 29;9(12):590. doi: 10.3390/genes9120590. Genes (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30501106 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular characterization and expression analysis of a complement component C3 in large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea).Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2015 Feb;42(2):272-9. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2014.11.006. Epub 2014 Nov 17. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25463300
-
Genome-Wide Association and Expression Analysis Revealed the Candidate Variants and Molecular Underpinnings of Cold-Stress Response in Large Yellow Croaker.Mar Biotechnol (NY). 2022 Oct;24(5):927-941. doi: 10.1007/s10126-022-10155-7. Epub 2022 Aug 15. Mar Biotechnol (NY). 2022. PMID: 35971020
-
Identification and expression profiles of ERK2 and ERK5 in large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea) after temperature stress and immune challenge.Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2015 Jun;44(2):410-9. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2015.03.006. Epub 2015 Mar 12. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25772549
-
Transcriptome analysis reveals molecular strategies in gills and heart of large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea) under hypoxia stress.Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020 Sep;104:304-313. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2020.06.028. Epub 2020 Jun 13. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32544557
Cited by
-
Leptin Gene Protects Against Cold Stress in Antarctic Toothfish.Front Physiol. 2021 Dec 15;12:740806. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2021.740806. eCollection 2021. Front Physiol. 2021. PMID: 34975517 Free PMC article.
-
Integration of mRNA and miRNA Profiling Reveals Heterosis in Oreochromis niloticus × O. aureus Hybrid Tilapia.Animals (Basel). 2022 Mar 3;12(5):640. doi: 10.3390/ani12050640. Animals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35268207 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen YY. The changes of mRNA expression of MIPS, SCD, CIRP in Pseudosciaena crocea under cold stress in related tissues. Ningbo University; Zhejiang: 2015.
-
- Chen K, Ding YP, Wang JL, Shao BP. Research progress on p53-involved metabolic regulation. Biotechnology Bulletin. 2016;32(11):52–58.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

