Silencing SAPCD2 Represses Proliferation and Lung Metastasis of Fibrosarcoma by Activating Hippo Signaling Pathway
- PMID: 33384953
- PMCID: PMC7770171
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2020.574383
Silencing SAPCD2 Represses Proliferation and Lung Metastasis of Fibrosarcoma by Activating Hippo Signaling Pathway
Abstract
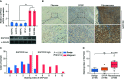
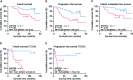
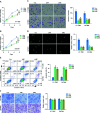
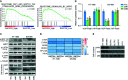
The primary problem associated with fibrosarcoma is its high potential to metastasize to the lung. Aberrant expression of SAPCD2 has been widely reported to be implicated in the progression and metastasis in multiple cancer types. However, the clinical significance and biological roles of SAPCD2 in fibrosarcoma remain unknown. Here, we reported that SAPCD2 expression was markedly elevated in fibrosarcoma tissues, and its expression was differentially upregulated in fibrosarcoma cell lines compared with that in several primary fibroblast cell lines. Kaplan-Meier survival analysis revealed that SAPCD2 overexpression was significantly correlated with early progression and metastasis, and poor prognosis in fibrosarcoma patients. Our results further showed that silencing SAPCD2 inhibited the proliferation and increased the apoptosis of fibrosarcoma cells in vitro. Importantly, silencing SAPCD2 repressed lung metastasis of fibrosarcoma cells in vivo. Mechanistic investigation further demonstrated that silencing SAPCD2 inhibited the proliferation and lung metastasis of fibrosarcoma cells by activating the Hippo signaling pathway, as evidenced by the finding that constitutively active YAP1, YAP1-S127A, significantly reversed the inhibitory effect of SAPCD2 downregulation on the colony formation and anchorage-independent growth capabilities of fibrosarcoma cells, as well as the stimulatory effect on the apoptotic ratio of fibrosarcoma cells. In conclusion, SAPCD2 promotes the proliferation and lung metastasis of fibrosarcoma cells by regulating the activity of Hippo signaling, and this mechanism represents a potential therapeutic target for the treatment of lung metastatic fibrosarcoma.
Keywords: Hippo signaling; SAPCD2; fibrosarcoma; lung metastasis; proliferation.
Copyright © 2020 Zhu, Wu, Niu, Yao, Xue, Wang, Yang, Li and Fan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Long noncoding RNA PXN-AS1-L promotes the malignancy of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells via upregulation of SAPCD2.Cancer Med. 2019 Aug;8(9):4278-4291. doi: 10.1002/cam4.2227. Epub 2019 Jun 7. Cancer Med. 2019. PMID: 31173488 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of SAPCD2 correlates with proliferation and invasion of colorectal carcinoma cells.Cancer Cell Int. 2020 Feb 6;20:43. doi: 10.1186/s12935-020-1121-6. eCollection 2020. Cancer Cell Int. 2020. PMID: 32055236 Free PMC article.
-
Disruption of LTBP4 Inhibition-Induced TGFβ1 Activation Promoted Cell Proliferation and Metastasis in Skin Melanoma by Inhibiting the Activation of the Hippo-YAP1 Signaling Pathway.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Feb 17;9:673904. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.673904. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35252214 Free PMC article.
-
The Function and Regulation of SAPCD2 in Physiological and Oncogenic Processes.J Cancer. 2022 Apr 18;13(7):2374-2387. doi: 10.7150/jca.65949. eCollection 2022. J Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35517423 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Progressive insights into fibrosarcoma diagnosis and treatment: leveraging fusion genes for advancements.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023 Oct 18;11:1284428. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1284428. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 37920823 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Curcumin alters distinct molecular pathways in breast cancer subtypes revealed by integrated miRNA/mRNA expression analysis.Cancer Rep (Hoboken). 2022 Oct;5(10):e1596. doi: 10.1002/cnr2.1596. Epub 2022 Jan 4. Cancer Rep (Hoboken). 2022. PMID: 34981672 Free PMC article.
-
Target Mechanisms of the Cyanotoxin Cylindrospermopsin in Immortalized Human Airway Epithelial Cells.Toxins (Basel). 2022 Nov 11;14(11):785. doi: 10.3390/toxins14110785. Toxins (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36422959 Free PMC article.
-
SAPCD2 promotes neuroblastoma progression by altering the subcellular distribution of E2F7.Cell Death Dis. 2022 Feb 23;13(2):174. doi: 10.1038/s41419-022-04624-z. Cell Death Dis. 2022. PMID: 35197448 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive Bioinformatics Analyses and Experimental Validation of the Cell Cycle Related Protein SAPCD2 as a New Biomarker and Potential Therapeutic Target in Pancreatic Cancer.J Inflamm Res. 2025 Feb 26;18:2855-2877. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S501850. eCollection 2025. J Inflamm Res. 2025. PMID: 40034688 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic Analysis and Biomarkers Identification of Immune Infiltration in Early and Late Stage Hepatocellular Carcinoma Based on TCGA Data.Int J Gen Med. 2023 Jun 16;16:2519-2530. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S420458. eCollection 2023. Int J Gen Med. 2023. PMID: 37346812 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Toro JR, Travis LB, Wu HJ, Zhu K, Fletcher CD, Devesa SS. Incidence patterns of soft tissue sarcomas, regardless of primary site, in the surveillance, epidemiology and end results program, 1978-2001: An analysis of 26,758 cases. Int J Cancer J Int Du Cancer (2006) 119:2922–30. 10.1002/ijc.22239 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

