Hemorrhagic shock necessitating resuscitation and damage control surgery after needle biopsy: A report of two cases
- PMID: 33385057
- PMCID: PMC7770969
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tcr.2020.100389
Hemorrhagic shock necessitating resuscitation and damage control surgery after needle biopsy: A report of two cases
Erratum in
-
Erratum regarding missing Patient Consent statement in previously published articles.Trauma Case Rep. 2023 Mar 1;45:100816. doi: 10.1016/j.tcr.2023.100816. eCollection 2023 Jun. Trauma Case Rep. 2023. PMID: 37234582 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Percutaneous needle biopsy is minimally invasive and widely performed. Bleeding is an important complication of needle biopsy. Because the wound created by the needle is small, the recognition of bleeding in the body may be delayed, and this delay can lead to hemorrhagic shock and death. We report two cases of hemorrhagic shock in which the trauma triad of death developed after needle biopsy and the patients required resuscitation and damage control surgery. Needle biopsy is less invasive but cannot stop bleeding, and so surgery should be considered to ensure hemostasis in a compromised patient.
Keywords: Damage control surgery; Deadly triad; Hemorrhagic shock; Needle biopsy.
© 2020 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
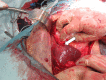

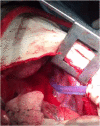

References
-
- Boyum J.H., Atwell T.D., Schmit G.D. Incidence and risk factors for adverse events related to image-guided liver biopsy. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2016;91:329–335. - PubMed
-
- Davis J.W., Mackersie R.C., Holbrook T.L., Hoyt D.B. Base deficit as an indicator of significant abdominal injury. Ann. Emerg. Med. 1991 Aug;20(8):842–844. - PubMed
-
- Ferrara A., MacArthur J.D., Wright H.K., Modlin I.M., McMillen M.A. Hypothermia and acidosis worsen coagulopathy in the patient requiring massive transfusion. Am. J. Surg. 1990 Nov;160(5):515–518. - PubMed
-
- Patel H.K., Khorana A.A. Anticoagulation in cancer patients: a summary of pitfalls to avoid. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2019;21(2):18. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

