Techno-economic analysis of aniline production via amination of phenol
- PMID: 33385086
- PMCID: PMC7772548
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e05778
Techno-economic analysis of aniline production via amination of phenol
Abstract
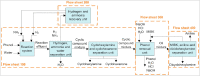
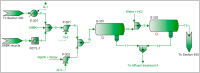
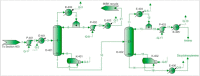
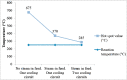
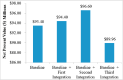
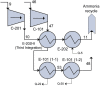
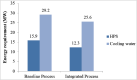
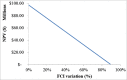
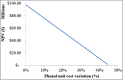
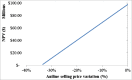
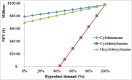
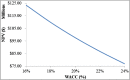
The purpose of this research is to demonstrate through a techno-economic assessment that aniline can be industrially produced using a profitable and inherently safer process than the ones currently employed. The aniline production process was designed using process simulation software. From this, the mass and energy balances were determined, the equipment sizing was performed and the net present value (NPV) was calculated to be USD 93.5 million. Additionally, a heat integration analysis was carried out in order to improve process profitability, obtaining a new NPV of USD 97.5 million. The economic sensitivity analysis showed that the process could withstand fixed capital investment changes of up to +89%, weighted average cost of capital changes between 16-24% and a decrease in cyclohexylamine demand of up to 44%. The conceptual design is still profitable when aniline price is varied in a range of 1224-1840 $/t and phenol cost in a range of 815-1178 $/t.
Keywords: Chemical engineering; Computer-aided engineering; Economic evaluation; Energy analysis; Industrial chemistry; Phenol to aniline; Process design; Process modeling; Process safety; Safety engineering.
© 2020 Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Process design, simulation, and techno-economic analysis of integrated production of furfural and glucose derived from palm oil empty fruit bunches.Clean Technol Environ Policy. 2023 Jan 7:1-17. doi: 10.1007/s10098-022-02454-3. Online ahead of print. Clean Technol Environ Policy. 2023. PMID: 36643617 Free PMC article.
-
Advanced process integration for supercritical production of biodiesel: Residual waste heat recovery via organic Rankine cycle (ORC).Renew Energy. 2021 Feb;164:433-443. doi: 10.1016/j.renene.2020.09.058. Epub 2020 Sep 18. Renew Energy. 2021. PMID: 32963424 Free PMC article.
-
Economic Evaluation and Techno-Economic Sensitivity Analysis of a Mass Integrated Shrimp Biorefinery in North Colombia.Polymers (Basel). 2020 Oct 18;12(10):2397. doi: 10.3390/polym12102397. Polymers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33080966 Free PMC article.
-
Process engineering economics of bioethanol production.Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol. 2007;108:303-27. doi: 10.1007/10_2007_063. Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol. 2007. PMID: 17541520 Review.
-
Techno-economic analysis of lignocellulosic ethanol: A review.Bioresour Technol. 2010 Jul;101(13):4980-91. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2010.02.009. Epub 2010 Mar 4. Bioresour Technol. 2010. PMID: 20206505 Review.
Cited by
-
Research and Developments of Heterogeneous Catalytic Technologies.Molecules. 2025 Aug 5;30(15):3279. doi: 10.3390/molecules30153279. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40807451 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Urinary and fecal excretion of aromatic amines in pet dogs and cats from the United States.Environ Int. 2022 May;163:107208. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2022.107208. Epub 2022 Mar 30. Environ Int. 2022. PMID: 35366557 Free PMC article.
-
One-Pot Catalytic Conversion of Lignin-Derivable Guaiacols and Syringols to Cyclohexylamines.ChemSusChem. 2022 Sep 20;15(18):e202200914. doi: 10.1002/cssc.202200914. Epub 2022 Aug 1. ChemSusChem. 2022. PMID: 35871610 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Agrawal R., Herron D.M. Optimal thermodynamic feed conditions for distillation of ideal binary mixtures. AIChE J. 1997;43:2984–2996.
-
- Alibaba . 2019. Shenyang East Chemical Science-Tech [WWW Document]. Cyclohexylamine Cas108-91-8.https://bit.ly/2Xl40jC URL.
-
- Alibaba . 2019. Haihang Industry Co. [WWW Document]. Stable Qual. Dicyclohexylamine.https://bit.ly/3eGiQak URL.
-
- Argyle M.D., Bartholomew C.H. Heterogeneous catalyst deactivation and regeneration: a review. Catalysts. 2015;5:145–269.
-
- Badeen C., Turcotte R., Hobenshield E., Berretta S. Thermal hazard assessment of nitrobenzene/dinitrobenzene mixtures. J. Hazard Mater. 2011;188:52–57. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

