Differences of time-dependent microRNA expressions in breast cancer cells
- PMID: 33385103
- PMCID: PMC7770513
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ncrna.2020.12.001
Differences of time-dependent microRNA expressions in breast cancer cells
Abstract
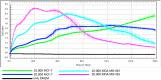
MicroRNA (miRNA) expression is a dynamic process in the cell, and the proper time period for post-transcriptional regulation might be critical due to the gene-on/-off expression times of the cell. Here, we investigated the effect of different time-points on proliferation, invasion and miRNA expression profiles of human breast cancer cell lines MCF-7 (non-metastatic, epithelium-like breast cancer cell line with oestrogen receptor (ER) positive (+) and human breast cancer cell lines MDA-MB-435 (metastatic, invasive, ER negative (-). For this purpose, MCF-7 and MDA-MB-435 cells were seeded different number in E-plate 16 for proliferation experiment using an electrical impedance-based real-time cell analyzer system (RTCA) for 168 h. Similarly, invasion potential of MCF-7 and MDA-MB-435 were determined by RTCA for 90 h. Total RNAs including miRNAs were isolated at 2, 4, 6, 12, 24, 48 h from the MCF-7 and MDA-MB-435 cells. Afterward, the quantitative 84 miRNA expressions of MCF-7 and MDA-MB-435 were analyzed by Fluidigm Microfluidic 96.96 Dynamic Array. The results of these study demonstrated that both proliferation potential and invasion capacity of MDA-MB-435 is higher than MCF-7 as time-dependent manner. Furthermore, we detected that up/down expressions of 32 miRNAs at all time points in MDA-MB-435 compared to MCF-7 (at least ten-fold increased). Because of the high number of miRNAs, we more closely evaluated the expression of six of them (miR-100-5p, miR-29a-3p, miR-130a-3p, miR-10a-5p, miR-10b-5p, miR-203a), and determined that their levels were dramatically changed by at least 50-fold at different time points of the experiment (p < 0.01). The expression levels of five of these miRNAs (miR-100-5p, miR-10a-5p, miR-10b-5p, miR-130a-3p, and miR-29a-3p) started to increase from the fourth hour and continued to increase until the 48th hour in MDA-MB-435 cells compared to MCF-7 cells (p < 0.01). Simultaneously, the expression of one of these miRNAs (miR-203a) decreased from the sixth hour to the 48th hour in MDA-MB-435 as compared to MCF-7. We determined pathways associated with target genes using mirPath - DIANA TOOLS. Small RNAs including miRNA are essential regulatory molecules for gene expressions. In the literature, gene expressions have been published as burst and pulse in the form of discontinuous transcription. The data of the research suggested that time-dependent changes of miRNA expressions can be affected target gene transcriptional fluctuations in breast cancer cell and can be base for the further studies.
Keywords: Discontinuous transcription; MCF-7; MDA-MB-435; miRNA.
© 2020 Production and hosting by Elsevier B.V. on behalf of KeAi Communications Co., Ltd.
Figures




References
-
- Han H.S., Magliocco A.M. Molecular testing and the pathologist's role in clinical trials of breast cancer. Clin. Breast Canc. 2016:166–179. - PubMed
-
- Makarova J., Shkurnikov M.U., Wicklein D. Intracellular and extracellular microRNA: an update on localization and biological role. Prog. Histochem. Cytochem. 2016:33–49. - PubMed
-
- Bartel Dp D.P. MicroRNAs genomics biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004:281–297. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

