Causal Relationship and Shared Genetic Loci between Psoriasis and Type 2 Diabetes through Trans-Disease Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 33385400
- PMCID: PMC8154633
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jid.2020.11.025
Causal Relationship and Shared Genetic Loci between Psoriasis and Type 2 Diabetes through Trans-Disease Meta-Analysis
Abstract
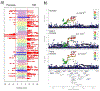
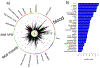
Psoriasis and type 2 diabetes (T2D) are complex conditions with significant impacts on health. Patients with psoriasis have a higher risk of T2D (∼1.5 OR) and vice versa, controlling for body mass index; yet, there has been a limited study comparing their genetic architecture. We hypothesized that there are shared genetic components between psoriasis and T2D. Trans-disease meta-analysis was applied to 8,016,731 well-imputed genetic markers from large-scale meta-analyses of psoriasis (11,024 cases and 16,336 controls) and T2D (74,124 cases and 824,006 controls), adjusted for body mass index. We confirmed our findings in a hospital-based study (42,112 patients) and tested for causal relationships with multivariable Mendelian randomization. Mendelian randomization identified a causal relationship between psoriasis and T2D (P = 1.6 × 10‒4, OR = 1.01) and highlighted the impact of body mass index. Trans-disease meta-analysis further revealed four genome-wide significant loci (P < 5 × 10‒8) with evidence of colocalization and shared directions of effect between psoriasis and T2D not present in body mass index. The proteins coded by genes in these loci (ACTR2, ERLIN1, TRMT112, and BECN1) are connected through NF-κB signaling. Our results provide insight into the immunological components that connect immune-mediated skin conditions and metabolic diseases, independent of confounding factors.
Copyright © 2021 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest
JEG received research grants from AbbVie, AnaptysBio, Pfizer, Novartis, Celgene, and Eli Lilly, and serves as advisory board in Novartis, AbbVie, Eli Lilly, MiRagen, and Almirall. NNM is a full-time US government employee and has served as a consultant for Amgen, Eli Lilly, and Leo Pharma receiving grants/other payments; as a principal investigator and/or investigator for AbbVie, Celgene, Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Inc, and Novartis receiving grants and/or research funding; and as a principal investigator for the National Institute of Health receiving grants and/or research funding.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Shared Genetic Risk Factors for Multiple Sclerosis/Psoriasis Suggest Involvement of Interleukin-17 and Janus Kinase-Signal Transducers and Activators of Transcription Signaling.Ann Neurol. 2023 Aug;94(2):384-397. doi: 10.1002/ana.26672. Epub 2023 May 18. Ann Neurol. 2023. PMID: 37127916 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic evidence for a causal relationship between type 2 diabetes and peripheral artery disease in both Europeans and East Asians.BMC Med. 2022 Aug 31;20(1):300. doi: 10.1186/s12916-022-02476-0. BMC Med. 2022. PMID: 36042491 Free PMC article.
-
Smoking Status and Type 2 Diabetes, and Cardiovascular Disease: A Comprehensive Analysis of Shared Genetic Etiology and Causal Relationship.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Feb 18;13:809445. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.809445. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35250867 Free PMC article.
-
Shared genetic etiology underlying Alzheimer's disease and type 2 diabetes.Mol Aspects Med. 2015 Jun-Oct;43-44:66-76. doi: 10.1016/j.mam.2015.06.006. Epub 2015 Jun 23. Mol Aspects Med. 2015. PMID: 26116273 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The current landscape of psoriasis genetics in 2020.J Dermatol Sci. 2020 Jul;99(1):2-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jdermsci.2020.05.008. Epub 2020 May 28. J Dermatol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32536600 Review.
Cited by
-
Break on through: The role of innate immunity and barrier defence in atopic dermatitis and psoriasis.Skin Health Dis. 2022 Feb 16;2(2):e99. doi: 10.1002/ski2.99. eCollection 2022 Jun. Skin Health Dis. 2022. PMID: 35677926 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Shared genetic risk factors and causal association between psoriasis and coronary artery disease.Nat Commun. 2022 Nov 2;13(1):6565. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-34323-4. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 36323703 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomics analysis of lung tissue reveals protein makers for the lung injury of adjuvant arthritis rats.Mol Med Rep. 2023 Sep;28(3):163. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2023.13051. Epub 2023 Jul 14. Mol Med Rep. 2023. PMID: 37449522 Free PMC article.
-
Autoimmune diseases and the risk and prognosis of latent autoimmune diabetes in adults.Diabetologia. 2025 Feb;68(2):331-341. doi: 10.1007/s00125-024-06303-4. Epub 2024 Oct 28. Diabetologia. 2025. PMID: 39467873 Free PMC article.
-
Multitrait genome-wide analyses identify new susceptibility loci and candidate drugs to primary sclerosing cholangitis.Nat Commun. 2023 Feb 24;14(1):1069. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-36678-8. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 36828809 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Badr D, Kurban M, Abbas O. Metformin in dermatology: an overview. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology : JEADV 2013;27(11):1329–35. - PubMed
-
- Balasubramanyam M, Aravind S, Gokulakrishnan K, Prabu P, Sathishkumar C, Ranjani H, et al. Impaired miR-146a expression links subclinical inflammation and insulin resistance in Type 2 diabetes. Molecular and cellular biochemistry 2011;351(1–2):197–205. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R56 DK062370/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K08 AR060802/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR042742/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI130025/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK062370/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK062370/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AR075043/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- K01 AR072129/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR054966/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR050511/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR065183/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR063611/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

