The activity of yeast Apn2 AP endonuclease at uracil-derived AP sites is dependent on the major carbon source
- PMID: 33386486
- PMCID: PMC8035244
- DOI: 10.1007/s00294-020-01141-4
The activity of yeast Apn2 AP endonuclease at uracil-derived AP sites is dependent on the major carbon source
Abstract
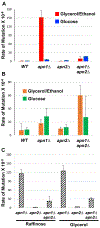
Yeast Apn2 is an AP endonuclease and DNA 3'-diesterase that belongs to the Exo III family with homology to the E. coli exonuclease III, Schizosaccharomyces pombe eth1, and human AP endonucleases APEX1 and APEX2. In the absence of Apn1, the major AP endonuclease in yeast, Apn2 can cleave the DNA backbone at an AP lesion initiating the base excision repair pathway. To study the role and relative contribution of Apn2, we took advantage of a reporter system that was previously used to delineate how uracil-derived AP sites are repaired. At this reporter, disruption of the Apn1-initiated base excision repair pathway led to a significant elevation of A:T to C:G transversions. Here we show that such highly elevated A:T to C:G transversion mutations associated with uracil residues in DNA are abolished when apn1∆ yeast cells are grown in glucose as the primary carbon source. We also show that the disruption of Apn2, either by the complete gene deletion or by the mutation of a catalytic residue, results in a similarly reduced rate of the uracil-associated mutations. Overall, our results indicate that Apn2 activity is regulated by the glucose repression pathway in yeast.
Keywords: AP endonuclease; DNA repair; Glucose repression; Uracil in DNA.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

