Preoperative prediction of the stage, size, grade, and necrosis score in clear cell renal cell carcinoma using MRI-based radiomics
- PMID: 33386910
- PMCID: PMC11193204
- DOI: 10.1007/s00261-020-02876-x
Preoperative prediction of the stage, size, grade, and necrosis score in clear cell renal cell carcinoma using MRI-based radiomics
Abstract
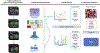
Purpose: Clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) is the most common subtype of renal cell carcinoma. Currently, there is a lack of noninvasive methods to stratify ccRCC prognosis prior to any invasive therapies. The purpose of this study was to preoperatively predict the tumor stage, size, grade, and necrosis (SSIGN) score of ccRCC using MRI-based radiomics.
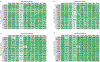
Methods: A multicenter cohort of 364 histopathologically confirmed ccRCC patients (272 low [< 4] and 92 high [≥ 4] SSIGN score) with preoperative T2-weighted and T1-contrast-enhanced MRI were retrospectively identified and divided into training (254 patients) and testing sets (110 patients). The performance of a manually optimized radiomics model was assessed by measuring accuracy, sensitivity, specificity, area under receiver operating characteristic curve (AUROC), and area under precision-recall curve (AUPRC) on an independent test set, which was not included in model training. Lastly, its performance was compared to that of a machine learning pipeline, Tree-Based Pipeline Optimization Tool (TPOT).
Results: The manually optimized radiomics model using Random Forest classification and Analysis of Variance feature selection methods achieved an AUROC of 0.89, AUPRC of 0.81, accuracy of 0.89 (95% CI 0.816-0.937), specificity of 0.95 (95% CI 0.875-0.984), and sensitivity of 0.72 (95% CI 0.537-0.852) on the test set. The TPOT using Extra Trees Classifier achieved an AUROC of 0.94, AUPRC of 0.83, accuracy of 0.89 (95% CI 0.816-0.937), specificity of 0.95 (95% CI 0.875-0.984), and sensitivity of 0.72 (95% CI 0.537-0.852) on the test set.
Conclusion: Preoperative MR radiomics can accurately predict SSIGN score of ccRCC, suggesting its promise as a prognostic tool that can be used in conjunction with diagnostic markers.
Keywords: Imaging analysis; Medical imaging; Neoplasm progression; Renal cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

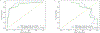
Similar articles
-
A preoperative CT-based deep learning radiomics model in predicting the stage, size, grade and necrosis score and outcome in localized clear cell renal cell carcinoma: A multicenter study.Eur J Radiol. 2023 Sep;166:111018. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2023.111018. Epub 2023 Jul 29. Eur J Radiol. 2023. PMID: 37562222
-
A CT-based deep learning radiomics nomogram outperforms the existing prognostic models for outcome prediction in clear cell renal cell carcinoma: a multicenter study.Eur Radiol. 2023 Dec;33(12):8858-8868. doi: 10.1007/s00330-023-09869-6. Epub 2023 Jun 30. Eur Radiol. 2023. PMID: 37389608
-
Development and validation of a CT-based nomogram for preoperative prediction of clear cell renal cell carcinoma grades.Eur Radiol. 2021 Aug;31(8):6078-6086. doi: 10.1007/s00330-020-07667-y. Epub 2021 Jan 29. Eur Radiol. 2021. PMID: 33515086
-
Multi-sequence MRI-based radiomics model to preoperatively predict the WHO/ISUP grade of clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma: a two-center study.BMC Cancer. 2024 Sep 27;24(1):1176. doi: 10.1186/s12885-024-12930-2. BMC Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39333970 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic test accuracy of ADC values for identification of clear cell renal cell carcinoma: systematic review and meta-analysis.Eur Radiol. 2020 Jul;30(7):4023-4038. doi: 10.1007/s00330-020-06740-w. Epub 2020 Mar 6. Eur Radiol. 2020. PMID: 32144458 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Normalization Strategies in Multi-Center Radiomics Abdominal MRI: Systematic Review and Meta-Analyses.IEEE Open J Eng Med Biol. 2023 Apr 28;4:67-76. doi: 10.1109/OJEMB.2023.3271455. eCollection 2023. IEEE Open J Eng Med Biol. 2023. PMID: 37283773 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting the WHO/ISUP Grade of Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma Through CT-Based Tumoral and Peritumoral Radiomics.Front Oncol. 2022 Feb 14;12:831112. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.831112. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35237524 Free PMC article.
-
A MRI-based radiomics nomogram for evaluation of renal function in ADPKD.Abdom Radiol (NY). 2022 Apr;47(4):1385-1395. doi: 10.1007/s00261-022-03433-4. Epub 2022 Feb 13. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2022. PMID: 35152314 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Validity of a multiphase CT-based radiomics model in predicting the Leibovich risk groups for localized clear cell renal cell carcinoma: an exploratory study.Insights Imaging. 2023 Oct 10;14(1):167. doi: 10.1186/s13244-023-01526-2. Insights Imaging. 2023. PMID: 37816901 Free PMC article.
-
Prediction study of surrounding tissue invasion in clear cell renal cell carcinoma based on multi-phase enhanced CT radiomics.Abdom Radiol (NY). 2025 Jun;50(6):2533-2548. doi: 10.1007/s00261-024-04712-y. Epub 2024 Nov 26. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2025. PMID: 39586898
References
-
- Garfield K, LaGrange CA (2020) Cancer, Renal Cell. In: StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing LLC. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470336/ Updated 2 August 2020. Accessed 27 September 2020.
-
- Klatte T, Rossi SH, Stewart GD (2018) Prognostic factors and prognostic models for renal cell carcinoma: a literature review. World J Urol 36(12): 1943–1952. - PubMed
-
- Frank I, Blute ML, Cheville JC, Lohse CM, Weaver AL, Zincke H (2002) An outcome prediction model for patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma treated with radical nephrectomy based on tumor stage, size, grade and necrosis: the SSIGN score. J Urol 168(6): 2395–400. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

