Relationship between chronic kidney disease and adverse outcomes of coronavirus disease 2019: a meta-analysis based on adjusted risk estimates
- PMID: 33387218
- PMCID: PMC7775836
- DOI: 10.1007/s11255-020-02748-9
Relationship between chronic kidney disease and adverse outcomes of coronavirus disease 2019: a meta-analysis based on adjusted risk estimates
Conflict of interest statement
All the authors declare that there is no potential conflict of interest.
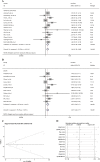
Figures
References
-
- Cen Y, Chen X, Shen Y, Zhang XH, Lei Y, Xu C, Jiang WR, Xu HT, Chen Y, Zhu J, Zhang LL, Liu YH. Risk factors for disease progression in patients with mild to moderate coronavirus disease 2019-a multi-centre observational study. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2020;S1198-1743X(1120):30341–30344. doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2020.05.041. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wang S, Ma P, Zhang S, Song S, Wang Z, Ma Y, Xu J, Wu F, Duan L, Yin Z, Luo H, Xiong N, Xu M, Zeng T, Jin Y. Fasting blood glucose at admission is an independent predictor for 28-day mortality in patients with COVID-19 without previous diagnosis of diabetes: a multi-centre retrospective study. Diabetologia. 2020 doi: 10.1007/s00125-020-05209-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Földi M, Farkas N, Kiss S, Zádori N, Váncsa S, Szakó L, Dembrovszky F, Solymár M, Bartalis E, Szakács Z, Hartmann P, Pár G, Erőss B, Molnár Z, Hegyi P, Szentesi A, Group KS. Obesity is a risk factor for developing critical condition in COVID-19 patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Obes Rev. 2020 doi: 10.1111/obr.13095. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Nandy K, Salunke A, Pathak SK, Pandey A, Doctor C, Puj K, Sharma M, Jain A, Warikoo V. Coronavirus disease (COVID-19): a systematic review and meta-analysis to evaluate the impact of various comorbidities on serious events. Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2020;14(5):1017–1025. doi: 10.1016/j.dsx.2020.06.064. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

