Acute kidney injury due to COVID-19 and the circadian rhythm
- PMID: 33387941
- PMCID: PMC7833969
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mehy.2020.110463
Acute kidney injury due to COVID-19 and the circadian rhythm
Abstract
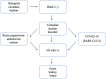
The COVID-19 pandemic caused by the novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) affects several organs including the kidneys. When examining patients with acute kidney injury (AKI) due to COVID-19, it is important to consider the circadian rhythm because in addition to its biological clock function, disruption of the circadian rhythm has been reported to be associated with the pathogenesis of several disorders, including AKI. Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2), an important component of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS), displays circadian rhythmicity. Studies have shown that over-expression of human ACE2 increases the replication of SARS-CoV-2, which may lead to disruptions and tissue damage due to the suppression of the brain and muscle ARNT-like protein-1(Bmal1) gene and high pro-inflammatory cytokines expressions in the tissues. Therefore, understanding and regulating the circadian rhythm and expression pattern of the key components of RAAS can prevent or reduce the severity of acute kidney injury that may occur with COVID-19 infection.
Keywords: Acute kidney injury; Bmal1; COVID-19; Circadian rhythm; Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Zhu N., Zhang D., Wang W., Li X., Yang B.o., Song J., Zhao X., Huang B., Shi W., Lu R., Niu P., Zhan F., Ma X., Wang D., Xu W., Wu G., Gao G.F., Tan W. A novel coronavirus from patients with pneumonia in China, 2019. N Engl J Med. 2020;382(8):727–733. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2001017. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hoffmann M., Kleine-Wever H., Kruger N., Muller M., Drotsten C., Pholhlmann S. The novel coronavirus 2019 (2019-nCoV) uses the SARS coronavirus receptor ACE2 and the cellular protease TMPRSS2 for entry in target cells. Cell. 2020;181:1–10. doi: 10.1101/2020.01.31.929042. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

