Impact of COVID-19 pandemic on the management of paediatric inflammatory bowel disease: An Italian multicentre study on behalf of the SIGENP IBD Group
- PMID: 33388247
- PMCID: PMC7832380
- DOI: 10.1016/j.dld.2020.12.011
Impact of COVID-19 pandemic on the management of paediatric inflammatory bowel disease: An Italian multicentre study on behalf of the SIGENP IBD Group
Abstract
Background: IBD management has been significantly affected during the COVID-19 lockdown with potential clinical issues.
Aims: The aim of this study was to analyse the impact of COVID-19 pandemic on the Italian paediatric IBD cohort.
Methods: This was a multicentre, retrospective, cohort investigation including 21 different Italian IBD referral centres. An electronic data collection was performed among the participating centres including: clinical characteristics of IBD patients, number of COVID-19 cases and clinical outcomes, disease management during the lockdown and the previous 9 weeks.
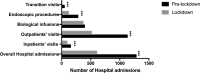
Results: 2291 children affected by IBD were enrolled. We experienced a significant reduction of the hospital admissions [604/2291 (26.3%) vs 1281/2291 (55.9%); p < 0.001]. More specifically, we observed a reduction of hospitalizations for new diagnosis (from n = 44 to n = 27) and endoscopic re-evaluations (from n = 46 to n = 8). Hospitalization for relapses and surgical procedures remained substantially unchanged. Biologic infusions did not significantly vary [393/2291 (17.1%) vs 368/2291 (16%); p = 0.3]. Telemedicine services for children with IBD were activated in 52.3% of the centres. In 42/2291(1.8%) children immunosuppressive therapies were adapted due to the concurrent COVID-19 pandemic.
Conclusion: Due to the several limitations of the lockdown, cares for children with IBD have been kept to minimal standards, giving priorities to the urgencies and to biologics' infusions and implementing telemedicine services.
Keywords: COVID-19; Inflammatory Bowel Disease; Paediatrics; immunosuppression; lockdown; telemedicine.
Copyright © 2020 Editrice Gastroenterologica Italiana S.r.l. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors have no conflict of interests to declare with regards to this manuscript.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Impact of the COVID-19 outbreak and the serum prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 antibodies in patients with inflammatory bowel disease treated with biologic drugs.Dig Liver Dis. 2021 Mar;53(3):277-282. doi: 10.1016/j.dld.2020.12.120. Epub 2021 Jan 6. Dig Liver Dis. 2021. PMID: 33423942 Free PMC article.
-
COVID-19 in IBD: The experience of a single tertiary IBD center.Dig Liver Dis. 2021 Mar;53(3):271-276. doi: 10.1016/j.dld.2020.12.012. Epub 2020 Dec 26. Dig Liver Dis. 2021. PMID: 33451910 Free PMC article.
-
How to manage inflammatory bowel disease during the COVID-19 pandemic: A guide for the practicing clinician.World J Gastroenterol. 2021 Mar 21;27(11):1022-1042. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i11.1022. World J Gastroenterol. 2021. PMID: 33776370 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inflammatory Bowel Disease Management in a Romanian Tertiary Gastroenterology Center: Challenges of the COVID-19 Pandemic.J Gastrointestin Liver Dis. 2020 Dec 12;29(4):549-553. doi: 10.15403/jgld-3183. J Gastrointestin Liver Dis. 2020. PMID: 33331349
-
Optimal inflammatory bowel disease management during the global coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic.Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2021 Jul 1;37(4):313-319. doi: 10.1097/MOG.0000000000000741. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2021. PMID: 33859104 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A Multifaced Aspect of Clostridium difficile Infection in Pediatric Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Case Series and Literature Review.J Pers Med. 2023 Sep 20;13(9):1413. doi: 10.3390/jpm13091413. J Pers Med. 2023. PMID: 37763180 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hospitalisation for Drug Infusion Did Not Increase Levels of Anxiety and the Risk of Disease Relapse in Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease during COVID-19 Outbreak.J Clin Med. 2021 Jul 24;10(15):3270. doi: 10.3390/jcm10153270. J Clin Med. 2021. PMID: 34362053 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of COVID-19 pandemic on pediatric endoscopy: A multicenter study on behalf of the SIGENP Endoscopy Working Group.Dig Liver Dis. 2022 May;54(5):572-579. doi: 10.1016/j.dld.2022.02.010. Epub 2022 Mar 9. Dig Liver Dis. 2022. PMID: 35361566 Free PMC article.
-
Gastrointestinal involvement in paediatric COVID-19 - from pathogenesis to clinical management: A comprehensive review.World J Gastroenterol. 2021 Jun 21;27(23):3303-3316. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i23.3303. World J Gastroenterol. 2021. PMID: 34163113 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Telemonitoring in adolescents with inflammatory bowel disease: a systematic review.Eur J Pediatr. 2025 Aug 5;184(8):531. doi: 10.1007/s00431-025-06341-z. Eur J Pediatr. 2025. PMID: 40764466 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Rosenbaum L. Facing Covid-19 in Italy - ethics, logistics, and therapeutics on the epidemic's front line. N Engl J Med. 2020;382:1873–1875. - PubMed
-
- John Hopkins University; 2020. Coronavirus Resource Center coronavirus COVID-19 global cases. https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/map.htmlaccessed August 27th 2020.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical