Downregulation of lncRNA TSLNC8 promotes melanoma resistance to BRAF inhibitor PLX4720 through binding with PP1α to re-activate MAPK signaling
- PMID: 33389075
- PMCID: PMC11802067
- DOI: 10.1007/s00432-020-03484-4
Downregulation of lncRNA TSLNC8 promotes melanoma resistance to BRAF inhibitor PLX4720 through binding with PP1α to re-activate MAPK signaling
Abstract
Purpose: Approximately 60% of patients with melanoma harbor BRAF mutation and targeting BRAF offers enormous advance in the treatment of those patients. Unfortunately, the efficacy of the BRAF inhibitors is usually restricted by the onset of drug resistance. Therefore, better understanding of the adaptive drug resistance mechanisms is essential for the development of alternative therapeutic strategies, and offers more promising measures to promote the short duration of response to BRAF inhibitors.
Methods: The levels of tumor suppressive long noncoding RNA on chromosome 8p12 (TSLNC8) were evaluated by qPCR. The MTT assay, colony formation assay, apoptosis assay, and in vivo xenograft tumor model were performed to assess the functions of TSLNC8 on drug resistance. Western blotting, RNA pull-down, and RNA immunoprecipitation (RIP) assays were applied to investigate the mechanisms of TSLNC8 in melanoma.
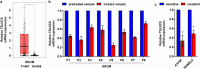
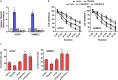
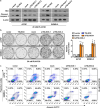
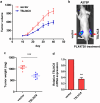
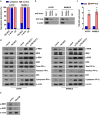
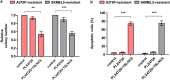
Results: Herein, our findings demonstrate that TSLNC8 is significantly downregulated in BRAF inhibitor-resistant melanoma tissues and cells. Moreover, downregulation of TSLNC8 in BRAF inhibitor sensitive cells reduces the toxicity response to BRAF inhibitor PLX4720, and inhibits apoptosis of melanoma cells-treated with PLX4720. Further assay elucidates that TSLNC8 can bind with the catalytic subunit of protein phosphatase 1α (PP1α) to regulate its distribution, and Downregulation of TSLNC8 results in PP1α cytoplasmic accumulation, thus re-activating the MAPK signaling. Eventually, the overexpression of TSLNC8 in BRAF inhibitor PLX4720-resistant melanoma cells restores the sensitive to BRAF inhibitor.
Conclusion: Collectively, our research provides a compelling rationale for resistance to BRAF inhibitor in melanoma, and the patient might benefit from the combinatorial therapy of BRAF inhibitors and lncRNA TSLNC8.
Keywords: BRAF mutation; MAPK signaling; PP1α; TSLNC8.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests of this study.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

