Heat-related illnesses in a mass gathering event and the necessity for newer diagnostic criteria: a field study
- PMID: 33389467
- PMCID: PMC7778691
- DOI: 10.1007/s11356-020-12154-4
Heat-related illnesses in a mass gathering event and the necessity for newer diagnostic criteria: a field study
Abstract
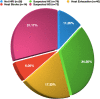
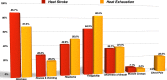
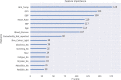
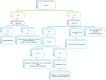
Heat-related illnesses (HRIs), mainly heat exhaustion (HE) and heat stroke (HS), are characterized by an elevation of core body temperature. In this study, we aimed to explore the HRIs' types and patient characteristics among a sample taken from various representative in-field points in the Hajj season. A cross-sectional study was conducted in 2018 at 80 data collection points distributed in the field. Data related to demographics, features and risk factors were collected and analyzed from all encountered cases with suspected HRIs. Moreover, we developed a diagnostic tree for HRIs by using the XGBoost model. Out of the 1200 persons encountered during the study period, 231 fulfilled the criteria of HRIs spectrum and were included in this study. Around 6% had HS and 20% had HE. All HS cases (100%) were from outside of Saudi Arabia as compared with 72.5% diagnosed with HE (27.5% were from Saudi Arabia). In addition, 16% were considered as heat-induced muscle spasms, and 7% had limb heat edema. Additionally, most of HRIs cases were reported between 11 am and 1 pm. The HRIs diagnostic tree model gave a diagnostic accuracy of 93.6%. This study highlights the magnitude of HRIs among pilgrims in Hajj and provides a diagnostic tree that can aid in the risk stratification and diagnosis of these patients. We advise the implementation of more educational campaigns to pilgrims regarding preventable measures especially for the vulnerable groups (e.g. from outside Saudi Arabia, those with comorbidities and light-skinned people).
Keywords: Crowds; Field study; HRIs; Hajj; Heat exhaustion; Heat stroke; Heat-related illnesses.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Risk factors for heat-related illnesses during the Hajj mass gathering: an expert review.Rev Environ Health. 2021 Oct 30;38(1):33-43. doi: 10.1515/reveh-2021-0097. Print 2023 Mar 28. Rev Environ Health. 2021. PMID: 34714988 Review.
-
Adherence of Healthcare Workers to Saudi Management Guidelines of Heat-Related Illnesses during Hajj Pilgrimage.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 Jan 28;18(3):1156. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18031156. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021. PMID: 33525576 Free PMC article.
-
Knowledge, Attitude and Practice of Pilgrims Regarding Heat-Related Illnesses during the 2017 Hajj Mass Gathering.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019 Sep 3;16(17):3215. doi: 10.3390/ijerph16173215. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019. PMID: 31484343 Free PMC article.
-
Perceptions of, and Practices for Coping with, Heat Exposure among Male Arab Pilgrims to the Hajj, 1436.Prehosp Disaster Med. 2019 Apr;34(2):161-174. doi: 10.1017/S1049023X19000025. Epub 2019 Apr 10. Prehosp Disaster Med. 2019. PMID: 30968815
-
Hajj and the Mental Health of Muslim Pilgrims: A review.Psychiatr Danub. 2019 Sep;31(Suppl 3):290-293. Psychiatr Danub. 2019. PMID: 31488742 Review.
Cited by
-
Knowledge, attitudes, and practices among the general community population toward heatstroke.Front Public Health. 2024 May 24;12:1373025. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1373025. eCollection 2024. Front Public Health. 2024. PMID: 38855448 Free PMC article.
-
Exertional heat stroke causes long-term skeletal muscle epigenetic reprogramming, altered gene expression, and impaired satellite cell function in mice.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2024 Feb 1;326(2):R160-R175. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00226.2023. Epub 2023 Dec 4. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2024. PMID: 38047316 Free PMC article.
-
Identity enactment as a social accomplishment: Shared identity and the provision of mutual support amongst pilgrims undertaking the Hajj.Br J Soc Psychol. 2025 Apr;64(2):e12796. doi: 10.1111/bjso.12796. Epub 2024 Aug 27. Br J Soc Psychol. 2025. PMID: 39189444 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying Knowledge Gaps Regarding Heat Stroke Among an Adult Sample in Pune, India: A Descriptive Analysis.Cureus. 2025 Apr 25;17(4):e82963. doi: 10.7759/cureus.82963. eCollection 2025 Apr. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40416226 Free PMC article.
-
The Impact of Fucoidan Extracts on Heat-Stress-Induced Loss of In Vitro Fast-Twitch Muscle Function in Mice.Muscles. 2025 Feb 27;4(1):6. doi: 10.3390/muscles4010006. Muscles. 2025. PMID: 40757581 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Al-Masud SMR, Bakar AA, Yussof SJSI (2016): Determining the types of diseases and emergency issues in Pilgrims during Hajj: a literature review. 5, 7
-
- Anonymous TimeandDate.com. Weather in August 2018 in Makkah, Saudi Arabia 2018
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

