Effects of Aging on Angiogenic and Muscle Growth-Related Factors in Naturally Aged Rat Skeletal Muscles
- PMID: 33389976
- PMCID: PMC7781957
- DOI: 10.4235/agmr.20.0077
Effects of Aging on Angiogenic and Muscle Growth-Related Factors in Naturally Aged Rat Skeletal Muscles
Abstract
Background: This study explored the effects of aging on the expression of angiogenic and muscle protein synthesis factors, as well as the number of satellite cells affecting sarcopenia in naturally aged rat skeletal muscles.
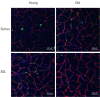
Methods: We divided 16 Sprague-Dawley rats into young (12 weeks old, n=8) and old (24 months old, n=8) groups and compared muscle and body weight (BW) between them. We also analyzed the expression levels of angiogenic and muscle growth proteins in soleus (slow-twitch) and extensor digitorum longus (EDL; fast-twitch) muscles by western blotting and assessed the number of skeletal muscle satellite cells and myonuclei and mean fiber cross-sectional area (CSA) using by immunofluorescence staining.
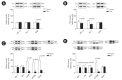
Results: EDL/BW was significantly lower in old rats than in young rats (p=0.002). The vascular endothelial growth factor level in soleus muscles was significantly lower in old rats than in young rats (p=0.001). Hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha and fetal liver kinase 1 levels in EDL muscles were lower in old rats than in young rats (p=0.001). The mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR), p70S6K, and 4E-BP1 levels were significantly lower in the soleus muscles of old rats than in those of young rats (p<0.01). Similarly, insulin growth factor-1, Akt, mTOR, and p70S6K levels were significantly lower in EDL muscles of old rats than in those of young rats (p<0.01). Additionally, myonuclei/fiber, Pax7/fiber, and mean fiber CSAs in both muscle types were significantly lower in old rats than in young rats (p<0.01).
Conclusion: Conclusion These data suggest different regulation of indices of angiogenic and muscle growth with aging in different muscle types.
Keywords: Angiogenesis; Muscle type; Protein synthesis; Vascular endothelial growth factor A; mTOR; Aging.
Conflict of interest statement
The researchers claim no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Rennie MJ. Anabolic resistance: the effects of aging, sexual dimorphism, and immobilization on human muscle protein turnover. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2009;34:377–81. - PubMed
-
- Burd NA, Wall BT, van Loon LJ. The curious case of anabolic resistance: old wives' tales or new fables? J Appl Physiol (1985) 2012;112:1233–5. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

