Pathogen-specific antimicrobials engineered de novo through membrane-protein biomimicry
- PMID: 33390588
- PMCID: PMC8131206
- DOI: 10.1038/s41551-020-00665-x
Pathogen-specific antimicrobials engineered de novo through membrane-protein biomimicry
Abstract
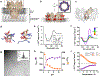
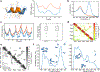
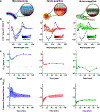
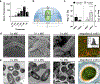
Precision antimicrobials aim to kill pathogens without damaging commensal bacteria in the host, and thereby cure disease without antibiotic-associated dysbiosis. Here we report the de novo design of a synthetic host defence peptide that targets a specific pathogen by mimicking key molecular features of the pathogen's channel-forming membrane proteins. By exploiting physical and structural vulnerabilities within the pathogen's cellular envelope, we designed a peptide sequence that undergoes instructed tryptophan-zippered assembly within the mycolic acid-rich outer membrane of Mycobacterium tuberculosis to specifically kill the pathogen without collateral toxicity towards lung commensal bacteria or host tissue. These mycomembrane-templated assemblies elicit rapid mycobactericidal activity and enhance the potency of antibiotics by improving their otherwise poor diffusion across the rigid M. tuberculosis envelope with respect to agents that exploit transmembrane protein channels for antimycobacterial activity. This biomimetic strategy may aid the design of other narrow-spectrum antimicrobial peptides.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Smillie CS et al. Ecology drives a global network of gene exchange connecting the human microbiome. Nature 480, 241 (2011). - PubMed
-
- Levy M, Blacher E & Elinav E Microbiome, metabolites and host immunity. Curr. Opin. Microbiol 35, 8–15 (2017). - PubMed
-
- Levy M, Kolodziejczyk AA, Thaiss CA & Elinav E Dysbiosis and the immune system. Nat. Rev. Immunol 17, 219 (2017). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

