Systematic and Comprehensive Automated Ventricle Segmentation on Ventricle Images of the Elderly Patients: A Retrospective Study
- PMID: 33390930
- PMCID: PMC7772233
- DOI: 10.3389/fnagi.2020.618538
Systematic and Comprehensive Automated Ventricle Segmentation on Ventricle Images of the Elderly Patients: A Retrospective Study
Abstract
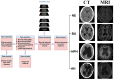
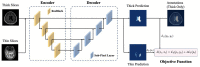
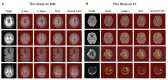
Background and Objective: Ventricle volume is closely related to hydrocephalus, brain atrophy, Alzheimer's, Parkinson's syndrome, and other diseases. To accurately measure the volume of the ventricles for elderly patients, we use deep learning to establish a systematic and comprehensive automated ventricle segmentation framework. Methods: The study participation included 20 normal elderly people, 20 patients with cerebral atrophy, 64 patients with normal pressure hydrocephalus, and 51 patients with acquired hydrocephalus. Second, get their imaging data through the picture archiving and communication systems (PACS) system. Then use ITK software to manually label participants' ventricular structures. Finally, extract imaging features through machine learning. Results: This automated ventricle segmentation method can be applied not only to CT and MRI images but also to images with different scan slice thicknesses. More importantly, it produces excellent segmentation results (Dice > 0.9). Conclusion: This automated ventricle segmentation method has wide applicability and clinical practicability. It can help clinicians find early disease, diagnose disease, understand the patient's disease progression, and evaluate the patient's treatment effect.
Keywords: computer tomography (CT); convolutional neural network (CNN); deep learning; image segmentation; magnetic resonance imaging; neuroimage; ventricular segmentation.
Copyright © 2020 Zhou, Ye, Jiang, Wang, Niu, Menpes-Smith, Fang, Liu, Xia and Yang.
Conflict of interest statement
ZN and WM-S are employed by Aladdin Healthcare Technologies Ltd. QY, YJ, and MW are employed by Hangzhou Ocean's Smart Boya Co., Ltd., China and Mind Rank Ltd., China. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
AI-based medical e-diagnosis for fast and automatic ventricular volume measurement in patients with normal pressure hydrocephalus.Neural Comput Appl. 2022 Feb 24;35(22):1-10. doi: 10.1007/s00521-022-07048-0. Online ahead of print. Neural Comput Appl. 2022. PMID: 35228779 Free PMC article.
-
Artificial intelligence for automatic cerebral ventricle segmentation and volume calculation: a clinical tool for the evaluation of pediatric hydrocephalus.J Neurosurg Pediatr. 2020 Dec 1;27(2):131-138. doi: 10.3171/2020.6.PEDS20251. Print 2021 Feb 1. J Neurosurg Pediatr. 2020. PMID: 33260138 Free PMC article.
-
Fully automated intracranial ventricle segmentation on CT with 2D regional convolutional neural network to estimate ventricular volume.Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg. 2019 Nov;14(11):1923-1932. doi: 10.1007/s11548-019-02038-5. Epub 2019 Jul 26. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg. 2019. PMID: 31350705
-
Postoperative glioma segmentation in CT image using deep feature fusion model guided by multi-sequence MRIs.Eur Radiol. 2020 Feb;30(2):823-832. doi: 10.1007/s00330-019-06441-z. Epub 2019 Oct 24. Eur Radiol. 2020. PMID: 31650265
-
Quantifying deep grey matter atrophy using automated segmentation approaches: A systematic review of structural MRI studies.Neuroimage. 2019 Nov 1;201:116018. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2019.116018. Epub 2019 Jul 15. Neuroimage. 2019. PMID: 31319182
Cited by
-
Deep learning-based segmentation of brain parenchyma and ventricular system in CT scans in the presence of anomalies.Front Neuroimaging. 2023 Aug 4;2:1228255. doi: 10.3389/fnimg.2023.1228255. eCollection 2023. Front Neuroimaging. 2023. PMID: 37554647 Free PMC article.
-
Deep Learning Achieves Neuroradiologist-Level Performance in Detecting Hydrocephalus Requiring Treatment.J Digit Imaging. 2022 Dec;35(6):1662-1672. doi: 10.1007/s10278-022-00654-3. Epub 2022 May 17. J Digit Imaging. 2022. PMID: 35581409 Free PMC article.
-
Deep learning for hydrocephalus prognosis: Advances, challenges, and future directions: A review.Medicine (Baltimore). 2025 Jun 27;104(26):e43082. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000043082. Medicine (Baltimore). 2025. PMID: 40587678 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Deep Learning-based Approach for Brainstem and Ventricular MR Planimetry: Application in Patients with Progressive Supranuclear Palsy.Radiol Artif Intell. 2024 May;6(3):e230151. doi: 10.1148/ryai.230151. Radiol Artif Intell. 2024. PMID: 38506619 Free PMC article.
-
AI-based medical e-diagnosis for fast and automatic ventricular volume measurement in patients with normal pressure hydrocephalus.Neural Comput Appl. 2022 Feb 24;35(22):1-10. doi: 10.1007/s00521-022-07048-0. Online ahead of print. Neural Comput Appl. 2022. PMID: 35228779 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

