Serotype Is Associated With High Rate of Colistin Resistance Among Clinical Isolates of Salmonella
- PMID: 33391208
- PMCID: PMC7775366
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.592146
Serotype Is Associated With High Rate of Colistin Resistance Among Clinical Isolates of Salmonella
Abstract
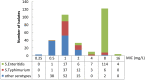
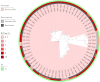
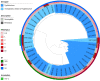
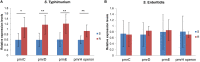
To investigate the prevalence, probable mechanisms and serotype correlation of colistin resistance in clinical isolates of Salmonella from patients in China, Salmonella isolates were collected from fecal and blood samples of patients. In this study, 42.8% (136/318) clinical isolated Salmonella were resistant to colistin. MIC distribution for colistin at serotype level among the two most prevalent serotypes originating from humans in China indicated that Salmonella Enteritidis (83.9% resistance, 125/149) were significantly less susceptible than Salmonella Typhimurium (15.3% resistance, 9/59, P < 0.01). mcr genes and mutations in PmrAB confer little for rate of colistin resistant Salmonella isolated from human patients. Phylogenetic tree based on core-genome single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) was separately by the serotypes and implied a diffused distribution of MICs in the same serotype isolates. Relatvie expression levels of colistin resistant related pmr genes were significantly higher in non-mcr colistin resistant S. Typhimurium than in colistin sensitive S. Typhimurium, but no discernable differences between colistin resistant and sensitive S. Enteritidis, indicating a different mechanism between colistin resistant S. Typhimurium and S. Enteritidis. In conclusion, colistin susceptibility and colistin resistant mechanism of clinical isolated Salmonella were closely associated with specific serotypes, at least in the two most prevalent serotype Enteritidis and Typhimurium. We suggest clinical microbiology laboratory interpreting Salmonella colistin MIC results in the serotype level.
Keywords: Salmonella enterica; clinical isolates; colistin susceptibility; phylogenetic analysis; pmr genes; serotype.
Copyright © 2020 Luo, Wang, Fu, Yu, Zheng, Chen, Berglund and Xiao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Colistin Resistance Mechanisms in Human Salmonella enterica Strains Isolated by the National Surveillance Enter-Net Italia (2016-2018).Antibiotics (Basel). 2022 Jan 13;11(1):102. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics11010102. Antibiotics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35052978 Free PMC article.
-
Tentative colistin epidemiological cut-off value for Salmonella spp.Foodborne Pathog Dis. 2012 Apr;9(4):367-9. doi: 10.1089/fpd.2011.1015. Epub 2012 Feb 2. Foodborne Pathog Dis. 2012. PMID: 22300222
-
Identification of Novel Mobilized Colistin Resistance Gene mcr-9 in a Multidrug-Resistant, Colistin-Susceptible Salmonella enterica Serotype Typhimurium Isolate.mBio. 2019 May 7;10(3):e00853-19. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00853-19. mBio. 2019. PMID: 31064835 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Detection of Integrons, Colistin and β-lactamase Resistant Genes in Salmonella enterica Serovars Enteritidis and Typhimurium Isolated from Chickens and Rats Inhabiting Poultry Farms.Microorganisms. 2022 Jan 28;10(2):313. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10020313. Microorganisms. 2022. PMID: 35208768 Free PMC article.
-
Mobile Colistin Resistance Genetic Determinants of Non-Typhoid Salmonella enterica Isolates from Russia.Microorganisms. 2021 Dec 4;9(12):2515. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms9122515. Microorganisms. 2021. PMID: 34946117 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The temporal dynamics of antimicrobial-resistant Salmonella enterica and predominant serovars in China.Natl Sci Rev. 2022 Nov 29;10(3):nwac269. doi: 10.1093/nsr/nwac269. eCollection 2023 Mar. Natl Sci Rev. 2022. PMID: 37035020 Free PMC article.
-
Global colistin use: a review of the emergence of resistant Enterobacterales and the impact on their genetic basis.FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2022 Feb 9;46(1):fuab049. doi: 10.1093/femsre/fuab049. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2022. PMID: 34612488 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Colistin Resistance Mechanisms in Human Salmonella enterica Strains Isolated by the National Surveillance Enter-Net Italia (2016-2018).Antibiotics (Basel). 2022 Jan 13;11(1):102. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics11010102. Antibiotics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35052978 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Borowiak M., Baumann B., Fischer J., Thomas K., Deneke C., Hammerl J. A., et al. (2020). Development of a novel mcr-6 to mcr-9 multiplex PCR and assessment of mcr-1 to mcr-9 occurrence in colistin-resistant Salmonella enterica isolates from environment, feed, animals and food (2011-2018) in Germany. Front. Microbiol. 11:80 10.3389/fmicb.2020.00080 - DOI - PMC - PubMed

