Loss of LIMCH1 predicts poor prognosis in patients with surgically resected Lung Adenocarcinoma: A study based on Immunohistochemical Analysis and Bioinformatics
- PMID: 33391414
- PMCID: PMC7738819
- DOI: 10.7150/jca.47883
Loss of LIMCH1 predicts poor prognosis in patients with surgically resected Lung Adenocarcinoma: A study based on Immunohistochemical Analysis and Bioinformatics
Abstract
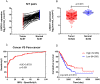
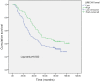
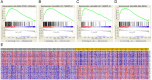
Background: LIMCH1, a novel actin-binding protein, is reported to correlate with tumorigenesis in multiple cancer types, but its clinical prognostic value in lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) patients remains unclear. Methods: A total of 196 patients with LUAD who underwent R0 resection were included for analysis. We integrated immunohistochemistry (IHC) and data mining analyses to determine LIMCH1 expression in tumor specimens; the chi-square test was used to explore the correlation between clinicopathologic factors and LIMCH1 expression in LUAD; Kaplan-Meier curves and the Cox proportional hazards model were used to investigate the clinical prognostic role of LIMCH1 expression in patients with LUAD; and DAVID enrichment and gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) were used to determine the underlying molecular mechanism. Results: LIMCH1 protein and mRNA expressions were significantly decreased in LUAD tissues. LIMCH1 mRNA expression was a potential diagnostic indicator in the TCGA cohort, and was associated with poor prognosis. IHC results in our LUAD cohort demonstrated that the LIMCH1 expression level was significantly associated with pleural invasion, tumor length, tumor differentiation grade, and clinical tumor stage. Patients with higher LIMCH1 expression had longer overall survival times. Cox multivariate survival analysis showed that LIMCH1 expression independently predicted the outcome. GO and KEGG clustering analyses showed that LIMCH1-related genes may be involved in 'cell adhesion', 'signal transduction', and several cancer-related pathways. GSEA showed 8 enriched hallmarks in the low LIMCH1 expression group, including mTOR signaling, MYC signaling, DNA repair, and G2M checkpoint. Conclusions: Our findings suggest that LIMCH1 may serve as a promising biomarker to predict LUAD prognosis.
Keywords: LIMCH1; TCGA; immunochemistry; lung adenocarcinoma; prognosis.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures


References
-
- Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD. et al. Cancer statistics in China, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 2016;66:115–32. - PubMed
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J Clin. 2020;70:7–30. - PubMed
-
- Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I. et al. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68:394–424. - PubMed
-
- Kaishang Z, Xue P, Shaozhong Z. et al. Elevated expression of Twinfilin-1 is correlated with inferior prognosis of lung adenocarcinoma. Life Sci. 2018;215:159–69. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

