Enhanced neprilysin-mediated degradation of hippocampal Aβ42 with a somatostatin peptide that enters the brain
- PMID: 33391505
- PMCID: PMC7738863
- DOI: 10.7150/thno.50263
Enhanced neprilysin-mediated degradation of hippocampal Aβ42 with a somatostatin peptide that enters the brain
Abstract
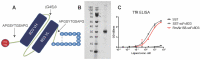
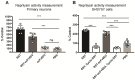
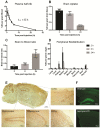
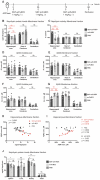
Background: Aggregation of the amyloid-beta (Aβ) peptide is one of the main neuropathological events in Alzheimer's disease (AD). Neprilysin is the major enzyme degrading Aβ, with its activity enhanced by the neuropeptide somatostatin (SST). SST levels are decreased in the brains of AD patients. The poor delivery of SST over the blood-brain barrier (BBB) and its extremely short half-life of only 3 min limit its therapeutic significance. Methods: We recombinantly fused SST to a BBB transporter binding to the transferrin receptor. Using primary neuronal cultures and neuroblastoma cell lines, the ability of the formed fusion protein to activate neprilysin was studied. SST-scFv8D3 was administered to mice overexpressing the Aβ-precursor protein (AβPP) with the Swedish mutation (APPswe) as a single injection or as a course of three injections over a 72 h period. Levels of neprilysin and Aβ were quantified using an Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Distribution of SST-scFv8D3 in the brain, blood and peripheral organs was studied by radiolabeling with iodine-125. Results: The construct, SST-scFv8D3, exhibited 120 times longer half-life than SST alone, reached the brain in high amounts when injected intravenously and significantly increased the brain concentration of neprilysin in APPswe mice. A significant decrease in the levels of membrane-bound Aβ42 was detected in the hippocampus and the adjacent cortical area after only three injections. Conclusion: With intravenous injections of our BBB permeable SST peptide, we were able to significantly increase the levels neprilysin, an effect that was followed by a significant and selective degradation of membrane-bound Aβ42 in the hippocampus. Being that membrane-bound Aβ triggers neuronal toxicity and the hippocampus is the central brain area in the progression of AD, the study has illuminated a new potential treatment paradigm with a promising safety profile targeting only the disease affected areas.
Keywords: Amyloid-β (Aβ) / blood-brain barrier (BBB) / neprilysin / somatostatin (SST) / transferrin receptor (TfR).
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Wide-Ranging Effects on the Brain Proteome in a Transgenic Mouse Model of Alzheimer's Disease Following Treatment with a Brain-Targeting Somatostatin Peptide.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2021 Jul 7;12(13):2529-2541. doi: 10.1021/acschemneuro.1c00303. Epub 2021 Jun 25. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34170117 Free PMC article.
-
Somatostatin therapy, neprilysin activation, and amyloid beta reduction: A novel approach for Alzheimer's treatment.Biomed Pharmacother. 2025 Aug;189:118325. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2025.118325. Epub 2025 Jul 8. Biomed Pharmacother. 2025. PMID: 40633205
-
Blood-brain barrier penetrating neprilysin degrades monomeric amyloid-beta in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease.Alzheimers Res Ther. 2022 Dec 5;14(1):180. doi: 10.1186/s13195-022-01132-2. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2022. PMID: 36471433 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding molecular mechanisms of proteolysis in Alzheimer's disease: progress toward therapeutic interventions.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2005 Aug 1;1751(1):60-7. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2005.02.013. Epub 2005 Mar 17. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2005. PMID: 16054018 Review.
-
The nucleation growth and reversibility of Amyloid-beta deposition in vivo.J Alzheimers Dis. 2006 Nov;10(2-3):291-301. doi: 10.3233/jad-2006-102-313. J Alzheimers Dis. 2006. PMID: 17119294 Review.
Cited by
-
Amyloid Beta Dynamics in Biological Fluids-Therapeutic Impact.J Clin Med. 2021 Dec 20;10(24):5986. doi: 10.3390/jcm10245986. J Clin Med. 2021. PMID: 34945282 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PET Imaging in Preclinical Anti-Aβ Drug Development.Pharm Res. 2022 Jul;39(7):1481-1496. doi: 10.1007/s11095-022-03277-z. Epub 2022 May 2. Pharm Res. 2022. PMID: 35501533 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Brain-Targeting Bispecific-Multivalent Antibody Clears Soluble Amyloid-Beta Aggregates in Alzheimer's Disease Mice.Neurotherapeutics. 2022 Sep;19(5):1588-1602. doi: 10.1007/s13311-022-01283-y. Epub 2022 Aug 8. Neurotherapeutics. 2022. PMID: 35939261 Free PMC article.
-
Reducing neonatal Fc receptor binding enhances clearance and brain-to-blood ratio of TfR-delivered bispecific amyloid-β antibody.MAbs. 2024 Jan-Dec;16(1):2339337. doi: 10.1080/19420862.2024.2339337. Epub 2024 Apr 18. MAbs. 2024. PMID: 38634473 Free PMC article.
-
Clearing Amyloid-Beta by Astrocytes: The Role of Rho GTPases Signaling Pathways as Potential Therapeutic Targets.Brain Sci. 2024 Dec 10;14(12):1239. doi: 10.3390/brainsci14121239. Brain Sci. 2024. PMID: 39766438 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Jarrett JT, Berger EP, Lansbury PT. The carboxy terminus of the beta amyloid protein is critical for the seeding of amyloid formation: implications for the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease. Biochemistry. 1993;32:4693–7. - PubMed
-
- Selkoe DJ. Alzheimer's disease Is a synaptic failure. Science. 2002;298:789–91. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

