Postoperative Brown-Séquard syndrome: case report and review of the literature
- PMID: 33391637
- PMCID: PMC7765703
- DOI: 10.1093/jscr/rjaa460
Postoperative Brown-Séquard syndrome: case report and review of the literature
Abstract
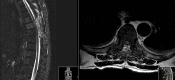
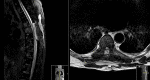
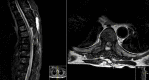
Brown-Séquard syndrome (BSS) is a rare neurological condition caused by a hemi-lesion of the spinal cord and was first described in the 1800s. BSS is characterized by an ipsilateral absence of motor control and discriminatory/proprioceptive/vibratory sensation at and below the spinal level involved, associated with loss of contralateral temperature and pain sensation a couple of vertebral segments below the lesion. BSS is commonly associated with trauma, but can also be iatrogenic. The authors report a case of a patient who presented with neoplastic dorsal spinal cord compression and developed a BSS after surgical decompression and review of the literature of postoperative BSS cases.
Published by Oxford University Press and JSCR Publishing Ltd. All rights reserved. © The Author(s) 2020.
Figures
References
-
- Lim E, Wong YS, Lo YL, Lim SH. Traumatic atypical Brown-Sequard syndrome: case report and literature review. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 2003;105:143–5. - PubMed
-
- Peacock WJ, Shrosbree RD, Key AG. A review of 450 stabwounds of the spinal cord. S Afr Med J 1977;51:961–4. - PubMed
-
- Oller DW, Boone S. Blunt Cervical Spine Brown-Séquard Injury. A Report of Three Cases. Am Surg 1991;57:361–5. - PubMed
-
- Herr RD, Barrett J. An unusual presentation of Brown-Sequard syndrome. Ann Emerg Med 1987;16:1285–8. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources