COVID-19-associated acute kidney injury: after the tubule and the glomerulus, now the vessel?
- PMID: 33391756
- PMCID: PMC7769511
- DOI: 10.1093/ckj/sfaa210
COVID-19-associated acute kidney injury: after the tubule and the glomerulus, now the vessel?
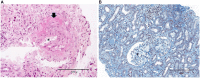
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

