Repeatability of proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy of the brain at 7 T: effect of scan time on semi-localized by adiabatic selective refocusing and short-echo time stimulated echo acquisition mode scans and their comparison
- PMID: 33392007
- PMCID: PMC7719915
- DOI: 10.21037/qims-20-517
Repeatability of proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy of the brain at 7 T: effect of scan time on semi-localized by adiabatic selective refocusing and short-echo time stimulated echo acquisition mode scans and their comparison
Abstract
Background: Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) provides a unique opportunity for in vivo measurements of the brain's metabolic profile. Two methods of mainstream data acquisition are compared at 7 T, which provides certain advantages as well as challenges. The two representative methods have seldom been compared in terms of measured metabolite concentrations and different scan times. The current study investigated proton MRS of the posterior cingulate cortex using a semi-localized by adiabatic selective refocusing (sLASER) sequence and a short echo time (TE) stimulated echo acquisition mode (sSTEAM) sequence, and it compared their reliability and repeatability at 7 T using a 32-channel head coil.
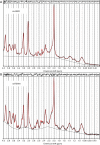
Methods: Sixteen healthy subjects were prospectively enrolled and scanned twice with an off-bed interval between scans. The scan parameters for sLASER were a TR/TE of 6.5 s/32 ms and 32 and 48 averages (sLASER×32 and sLASER×48, respectively). The scan parameters for sSTEAM were a TR/TE of 4 s/5 ms and 32, 48, and 64 averages (sSTEAM4×32, sSTEAM4×48, and sSTEAM4×64, respectively) in addition to that with a TR/TE of 8 s/5 ms and 32 averages (sSTEAM8×32). Data were analyzed using LCModel. Metabolites quantified with Cramér-Rao lower bounds (CRLBs) >50% were classified as not detected, and metabolites quantified with mean or median CRLBs ≤20% were included for further analysis. The SNR, CRLBs, coefficient of variation (CV), and metabolite concentrations were statistically compared using the Shapiro-Wilk test, one-way ANOVA, or the Friedman test.
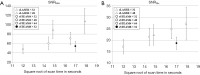
Results: The sLASER spectra for N-acetylaspartate + N-acetylaspartylglutamate (tNAA) and glutamate (Glu) had a comparable or higher SNR than sSTEAM spectra. Ten metabolites had lower CRLBs than prefixed thresholds: aspartate (Asp), γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA), glutamine (Gln), Glu, glutathione (GSH), myo-inositol (Ins), taurine (Tau), the total amount of phosphocholine + glycerophosphocholine (tCho), creatine + phosphocreatine (tCr), and tNAA. Performance of the two sequences was satisfactory except for GABA, for which sLASER yielded higher CRLBs (≥18%) than sSTEAM. Some significant differences in CRLBs were noted, but they were ≤2% except for GABA and Gln. Signal averaging significantly lowered CRLBs for some metabolites but only by a small amount. Measurement repeatability as indicated by median CVs was ≤10% for Gln, Glu, Ins, tCho, tCr, and tNAA in all scans, and that for Asp, GABA, GSH, and Tau was ≥10% under some scanning conditions. The CV for GABA according to sLASER was significantly higher than that according to sSTEAM, whereas the CV for Ins was higher according to sSTEAM. An increase in signal averaging contribute little to lower CVs except for Ins.
Conclusions: Both sequences quantified brain metabolites with a high degree of precision and repeatability. They are comparable except for GABA, for which sSTEAM would be a better choice.
Keywords: 7 Tesla (7 T); Cramér-Rao lower bound; Magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS); repeatability; semi-localized by adiabatic selective refocusing (sLASER); short echo time (TE) stimulated echo acquisition mode (sSTEAM).
2021 Quantitative Imaging in Medicine and Surgery. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure (available at http://dx.doi.org/10.21037/qims-20-517). TO serves as an unpaid editorial board member of Quantitative Imaging in Medicine and Surgery. TO reports grants from Siemens Healthcare K.K., during the conduct of the study; HK reports personal fees from Siemens Healthcare K.K. (Japan), during the conduct of the study; YU reports personal fees from Siemens Healthcare K.K. (Japan), during the conduct of the study; NS was a Siemens Research Collaboration manager in charge of MR Spectroscopy. NS retired in October 2017 and do not currently receive any salary from Siemens. RTS reports personal fees from Siemens Medical Solutions, USA Inc., during the conduct of the study; SA reports personal fees from Siemens Healthineers, during the conduct of the study. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Experimental Basis Sets of Quantification of Brain 1H-Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy at 3.0 T.Metabolites. 2023 Mar 1;13(3):368. doi: 10.3390/metabo13030368. Metabolites. 2023. PMID: 36984808 Free PMC article.
-
Improved resolution of glutamate, glutamine and γ-aminobutyric acid with optimized point-resolved spectroscopy sequence timings for their simultaneous quantification at 9.4 T.NMR Biomed. 2018 Jan;31(1). doi: 10.1002/nbm.3851. Epub 2017 Nov 3. NMR Biomed. 2018. PMID: 29105187
-
A comparison of sLASER and MEGA-sLASER using simultaneous interleaved acquisition for measuring GABA in the human brain at 7T.PLoS One. 2019 Oct 11;14(10):e0223702. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0223702. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31603925 Free PMC article.
-
Precision of metabolite-selective MRS measurements of glutamate, GABA and glutathione: A review of human brain studies.NMR Biomed. 2024 Mar;37(3):e5071. doi: 10.1002/nbm.5071. Epub 2023 Dec 4. NMR Biomed. 2024. PMID: 38050448 Review.
-
Meta-analysis of brain metabolite differences in HIV infection.Neuroimage Clin. 2020;28:102436. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2020.102436. Epub 2020 Sep 15. Neuroimage Clin. 2020. PMID: 33383609 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Test-retest reliability of multi-metabolite edited MRS at 3T using PRESS and sLASER.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Jun 11:2025.06.07.657685. doi: 10.1101/2025.06.07.657685. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40661367 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Reproducibility of 7-T brain spectroscopy using an ultrashort echo time STimulated Echo Acquisition Mode sequence and automated voxel repositioning.NMR Biomed. 2022 Feb;35(2):e4631. doi: 10.1002/nbm.4631. Epub 2021 Oct 8. NMR Biomed. 2022. PMID: 34622996 Free PMC article.
-
Intra- and inter-session reliability and repeatability of 1H magnetic resonance spectroscopy for determining total creatine concentrations in multiple brain regions.Exp Physiol. 2025 Mar;110(3):464-477. doi: 10.1113/EP092252. Epub 2024 Dec 20. Exp Physiol. 2025. PMID: 39707690 Free PMC article.
-
Quantification of GABA concentration measured noninvasively in the human posterior cingulate cortex with 7 T ultra-short-TE MR spectroscopy.Magn Reson Med. 2023 Mar;89(3):886-897. doi: 10.1002/mrm.29514. Epub 2022 Nov 13. Magn Reson Med. 2023. PMID: 36372932 Free PMC article.
-
GABA, glutamate and excitatory-inhibitory ratios measured using short-TE STEAM MRS at 7-Tesla: Effects of macromolecule basis sets and baseline parameters.Heliyon. 2023 Jul 15;9(7):e18357. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e18357. eCollection 2023 Jul. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37539101 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
