Status epilepticus as an initial manifestation of hepatic encephalopathy: A case report
- PMID: 33392334
- PMCID: PMC7760455
- DOI: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i24.6480
Status epilepticus as an initial manifestation of hepatic encephalopathy: A case report
Abstract
Background: Status epilepticus in patients with hepatic encephalopathy (HE) is a rare but serious condition that is refractory to antiepileptic drugs, and current treatment plans are vague. Diagnosis may be difficult without a clear history of cirrhosis. Liver transplantation (LT) is effective to alleviate symptoms, however, there are few reports about LT in the treatment of status epilepticus with HE. To our knowledge, this is the first report of status epilepticus present as initial manifestation of HE.
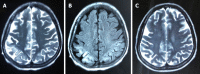
Case summary: A 59-year-old woman with a 20-year history of heavy drinking was hospitalized for generalized tonic-clonic seizures. She reported no history of episodes of HE, stroke, spontaneous bacterial peritonitis, ascites or gastrointestinal bleeding. Neurological examination revealed a comatose patient, without papilledema. Laboratory examination suggested liver cirrhosis. Plasma ammonia levels upon admission were five times normal. Brain computed tomography (CT) was normal, while abdominal CT and ultrasound revealed mild ascites, liver cirrhosis and splenomegaly. Electroencephalography (EEG)showed diffuse slow waves rhythm, consistent with HE, and sharp waves during ictal EEG corresponding to clinical semiology of focal tonic seizures. The symptoms were reversed by continuous antiepileptic treatment and lactulose. She was given oral levetiracetam, and focal aware seizures occasionally affected her 10 mo after LT.
Conclusion: Status epilepticus could be an initial manifestation of HE. Antiepileptic drugs combined with lactulose are essential for treatment of status epilepticus with HE, and LT is effective to prevent the relapse.
Keywords: Antiepileptic drugs; Case report; Decompensated alcoholic liver cirrhosis; Hepatic encephalopathy; Liver transplantation; Status epilepticus.
©The Author(s) 2020. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Status epilepticus as a manifestation of hepatic encephalopathy.Acta Neurol Scand. 2003 Feb;107(2):142-4. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0404.2003.02092.x. Acta Neurol Scand. 2003. PMID: 12580865
-
Hepatic encephalopathy with status epileptics: a case report.World J Gastroenterol. 2006 Mar 21;12(11):1793-4. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i11.1793. World J Gastroenterol. 2006. PMID: 16586556 Free PMC article.
-
Newly Diagnosed Hepatic Encephalopathy Presenting as Non-convulsive Status Epilepticus: A Case Report and Literature Review.Front Neurol. 2022 May 12;13:880068. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2022.880068. eCollection 2022. Front Neurol. 2022. PMID: 35645984 Free PMC article.
-
Refractory generalised convulsive status epilepticus : a guide to treatment.CNS Drugs. 2005;19(9):759-68. doi: 10.2165/00023210-200519090-00003. CNS Drugs. 2005. PMID: 16142991 Review.
-
Paraneoplastic Encephalopathy in a Patient With Metastatic Lung Cancer: A Case Study.J Adv Pract Oncol. 2018 Mar;9(2):216-221. Epub 2018 Mar 1. J Adv Pract Oncol. 2018. PMID: 30588355 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Vilstrup H, Amodio P, Bajaj J, Cordoba J, Ferenci P, Mullen KD, Weissenborn K, Wong P. Hepatic encephalopathy in chronic liver disease: 2014 Practice Guideline by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases and the European Association for the Study of the Liver. Hepatology. 2014;60:715–735. - PubMed
-
- Wijdicks EFM. Hepatic Encephalopathy. N Engl J Med. 2017;376:186. - PubMed
-
- ADAMS RD, FOLEY JM. The neurological disorder associated with liver disease. Res Publ Assoc Res Nerv Ment Dis. 1953;32:198–237. - PubMed
-
- Rudler M, Marois C, Weiss N, Thabut D, Navarro V Brain-Liver Pitié-Salpêtrière Study Group (BLIPS) Status epilepticus in patients with cirrhosis: How to avoid misdiagnosis in patients with hepatic encephalopathy. Seizure. 2017;45:192–197. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

