Endometrial extracellular matrix rigidity and IFNτ ensure the establishment of early pregnancy through activation of YAP
- PMID: 33393124
- PMCID: PMC7849163
- DOI: 10.1111/cpr.12976
Endometrial extracellular matrix rigidity and IFNτ ensure the establishment of early pregnancy through activation of YAP
Abstract
Background: In mammals, early pregnancy is a critical vulnerable period during which complications may arise, including pregnancy failure. Establishment of a maternal endometrial acceptance phenotype is a prerequisite for semiheterogeneous embryo implantation, comprising the rate-limiting step of early pregnancy.
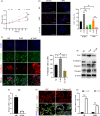
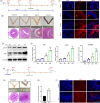
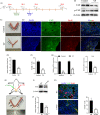
Methods: Confocal fluorescence, immunohistochemistry and western blot for nuclear and cytoplasmic protein were used to examine the activation of yes-associated protein (YAP) in uterine tissue and primary endometrial cells. The target binding between miR16a and YAP was verified by dual-luciferase reporter gene assay. The mouse pregnancy model and pseudopregnancy model were used to investigate the role of YAP in the maternal uterus during early pregnancy in vivo.
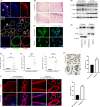
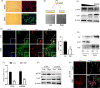
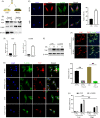
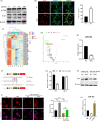
Results: We showed that YAP translocates into the nucleus in the endometrium of cattle and mice during early pregnancy. Mechanistically, YAP acts as a mediator of ECM rigidity and cell density, which requires the actomyosin cytoskeleton and is partially dependent on the Hippo pathway. Furthermore, we found that the soluble factor IFNτ, which is a ruminant pregnancy recognition factor, also induced activation of YAP by reducing the expression of miR-16a.
Conclusions: This study revealed that activation of YAP is necessary for early pregnancy in bovines because it induced cell proliferation and established an immunosuppressive local environment that allowed conceptus implantation into the uterine epithelium.
Keywords: IFNτ; Mechanoresponses; YAP; endometrium; pregnancy.
© 2021 The Authors. Cell Proliferation Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
References
-
- Chapron C, Marcellin L, Borghese B, Santulli P. Rethinking mechanisms, diagnosis and management of endometriosis. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2019;15(11):666‐682. - PubMed
-
- Zhang H, Wang S, Zhang S, Wang T, Deng X. Increasing trend of prevalence of infertility in Beijing. Chin Med J (Engl). 2014;127(4):691‐695. - PubMed
-
- Yuan M, Hu M, Lou Y, et al. Environmentally relevant levels of bisphenol A affect uterine decidualization and embryo implantation through the estrogen receptor/serum and glucocorticoid‐regulated kinase 1/epithelial sodium ion channel alpha‐subunit pathway in a mouse model. Fertil Steril. 2018;109(4):735‐744.e731. - PubMed
-
- Ma H, Zhai J, Wan H, et al. In vitro culture of cynomolgus monkey embryos beyond early gastrulation. Science. 2019;366(6467):eaax7890. - PubMed
-
- Niu Y, Sun N, Li C, et al. Dissecting primate early post‐implantation development using long‐term in vitro embryo culture. Science. 2019;366(6467):eaaw5754. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

