Botulinum toxin injection into the intrinsic laryngeal muscles to treat spasmodic dysphonia: A multicenter, placebo-controlled, randomized, double-blinded, parallel-group comparison/open-label clinical trial
- PMID: 33393175
- PMCID: PMC8248427
- DOI: 10.1111/ene.14714
Botulinum toxin injection into the intrinsic laryngeal muscles to treat spasmodic dysphonia: A multicenter, placebo-controlled, randomized, double-blinded, parallel-group comparison/open-label clinical trial
Abstract
Background and purpose: Botulinum toxin (BT) injection into the laryngeal muscles has been a standard treatment for spasmodic dysphonia (SD). However, few high-quality clinical studies have appeared, and BT is used off-label in most countries.
Methods: We performed a multicenter, placebo-controlled, randomized, double-blinded, parallel-group comparison/open-label clinical trial to obtain approval for BT (Botox) therapy in Japan. Twenty-four patients (22 with adductor SD and two with abductor SD) were enrolled. The primary end point was the change in the number of aberrant morae (phonemes) at 4 weeks after drug injection. The secondary end points included the change in the number of aberrant morae, GRBAS scale, Voice Handicap Index (VHI), and visual analog scale (VAS) over the entire study period.
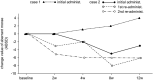
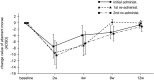
Results: In the adductor SD group, the number of aberrant morae at 4 weeks after injection was reduced by 7.0 ± 2.30 (mean ± SE) in the BT group and 0.2 ± 0.46 in the placebo group (p = 0.0148). The improvement persisted for 12 weeks following BT injections. The strain element in GRBAS scale significantly reduced at 2 weeks after BT treatment. The VHI and VAS scores as subjective parameters also improved. In the abductor SD group, one patient responded to treatment. Adverse events included breathy hoarseness (77.3%) and aspiration when drinking (40.9%) but were mild and resolved in 4 weeks.
Conclusions: Botulinum toxin injection was safe and efficacious for the treatment of SD. Based on these results, BT injection therapy was approved as an SD treatment in Japan.
Keywords: Voice Handicap Index; aberrant morae; botulinum toxin therapy; placebo-controlled double-blinded clinical trial; spasmodic dysphonia.
© 2021 The Authors. European Journal of Neurology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of European Academy of Neurology.
Conflict of interest statement
No author has any competing interest. Allergan supported the clinical trial by providing the investigational drug and placebo. GlaxoSmithKline KK provided pharmacological and safety information on Botox and scientific advice pertaining to the conduct of the study, and applied for BT approval to the PMDA after the trial. However, no author or institution received any financial support from either company, nor were they involved in the data collection, analysis and interpretation, study management, or manuscript preparation.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Botulinum Toxin Therapy for Spasmodic Dysphonia in Japan: The History and an Update.Toxins (Basel). 2022 Jul 1;14(7):451. doi: 10.3390/toxins14070451. Toxins (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35878189 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Botulinum Toxin Therapy: A Series of Clinical Studies on Patients with Spasmodic Dysphonia in Japan.Toxins (Basel). 2021 Nov 25;13(12):840. doi: 10.3390/toxins13120840. Toxins (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34941678 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Post-treatment clinical course following botulinum toxin injection therapy for adductor spasmodic dysphonia: Analysis of data from a placebo-controlled, randomized, double-blinded clinical trial in Japan.Laryngoscope Investig Otolaryngol. 2021 Sep 28;6(5):1088-1095. doi: 10.1002/lio2.669. eCollection 2021 Oct. Laryngoscope Investig Otolaryngol. 2021. PMID: 34667852 Free PMC article.
-
Quality of Life After Botulinum Toxin Injection in Patients With Adductor Spasmodic Dysphonia; a Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.J Voice. 2021 Mar;35(2):271-283. doi: 10.1016/j.jvoice.2019.07.025. Epub 2019 Aug 30. J Voice. 2021. PMID: 31477348
-
Botulinum toxin treatment of false vocal folds in adductor spasmodic dysphonia: Functional outcomes.Laryngoscope. 2016 Jan;126(1):118-21. doi: 10.1002/lary.25515. Epub 2015 Oct 15. Laryngoscope. 2016. PMID: 26467807
Cited by
-
Botulinum Toxin Therapy for Spasmodic Dysphonia in Japan: The History and an Update.Toxins (Basel). 2022 Jul 1;14(7):451. doi: 10.3390/toxins14070451. Toxins (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35878189 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Safety and Effectiveness of OnabotulinumtoxinA in Patients with Laryngeal Dystonia: Final Report of a 52-Week, Multicenter Postmarketing Surveillance Study.Toxins (Basel). 2023 Sep 5;15(9):553. doi: 10.3390/toxins15090553. Toxins (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37755979 Free PMC article.
-
Botulinum Toxin Therapy: A Series of Clinical Studies on Patients with Spasmodic Dysphonia in Japan.Toxins (Basel). 2021 Nov 25;13(12):840. doi: 10.3390/toxins13120840. Toxins (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34941678 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Guidelines for the Use of Botulinum Toxin in Otolaryngology From the Korean Society of Laryngology, Phoniatrics and Logopedics Guideline Task Force.Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol. 2023 Nov;16(4):291-307. doi: 10.21053/ceo.2023.00458. Epub 2023 Oct 25. Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol. 2023. PMID: 37905325 Free PMC article.
-
Post-treatment clinical course following botulinum toxin injection therapy for adductor spasmodic dysphonia: Analysis of data from a placebo-controlled, randomized, double-blinded clinical trial in Japan.Laryngoscope Investig Otolaryngol. 2021 Sep 28;6(5):1088-1095. doi: 10.1002/lio2.669. eCollection 2021 Oct. Laryngoscope Investig Otolaryngol. 2021. PMID: 34667852 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Blitzer A, Brin MF, Fahn S, Lovelace RE. Clinical and laboratory characteristics of laryngeal dystonia: a study of 110 cases. Laryngoscope. 1988;98:636‐640. - PubMed
-
- Aronson AE, Bless DM. Spasmodic dysphonia, Clinical Voice Disorders, 4th edn. New York, NY: Thieme Med Publ; 2009:101‐133.
-
- Blitzer A. Spasmodic dystonia and botulinum toxin: experience from the largest treatment series. Eur J Neurol. 2010;17(Suppl 1):28‐30. - PubMed
-
- Patel AB, Bansberg SF, Adler CH, Lott DG, Crujido L. The Mayo Clinic Arizona spasmodic dysphonia experience: a demographic analysis of 718 patients. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2015;124:859‐863. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

