Overcoming innate immune barriers that impede AAV gene therapy vectors
- PMID: 33393506
- PMCID: PMC7773343
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI143780
Overcoming innate immune barriers that impede AAV gene therapy vectors
Abstract
The field of gene therapy has made considerable progress over the past several years. Adeno-associated virus (AAV) vectors have emerged as promising and attractive tools for in vivo gene therapy. Despite the recent clinical successes achieved with recombinant AAVs (rAAVs) for therapeutics, host immune responses against the vector and transgene product have been observed in numerous preclinical and clinical studies. These outcomes have hampered the advancement of AAV gene therapies, preventing them from becoming fully viable and safe medicines. The human immune system is multidimensional and complex. Both the innate and adaptive arms of the immune system seem to play a concerted role in the response against rAAVs. While most efforts have been focused on the role of adaptive immunity and developing ways to overcome it, the innate immune system has also been found to have a critical function. Innate immunity not only mediates the initial response to the vector, but also primes the adaptive immune system to launch a more deleterious attack against the foreign vector. This Review highlights what is known about innate immune responses against rAAVs and discusses potential strategies to circumvent these pathways.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
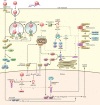
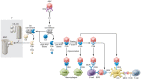
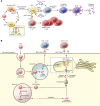
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- UG3 HL147367/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI067497/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI141181/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AI100263/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS076991/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI128358/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL097088/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AI067497/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R33 AI136007/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL131471/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI149646/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AI067497/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

