NF-κB signalling as a pharmacological target in COVID-19: potential roles for IKKβ inhibitors
- PMID: 33394134
- PMCID: PMC7780215
- DOI: 10.1007/s00210-020-02035-5
NF-κB signalling as a pharmacological target in COVID-19: potential roles for IKKβ inhibitors
Abstract
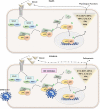
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) has been characterized by lymphopenia as well as a proinflammatory cytokine storm, which are responsible for the poor prognosis and multiorgan defects. The transcription factor nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) modulates the functions of the immune cells and alters the gene expression profile of different cytokines in response to various pathogenic stimuli, while many proinflammatory factors have been known to induce NF-κB signalling cascade. Besides, NF-κB has been known to potentiate the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) leading to apoptosis in various tissues in many diseases and viral infections. Though the reports on the involvement of the NF-κB signalling pathway in COVID-19 are limited, the therapeutic benefits of NF-κB inhibitors including dexamethasone, a synthetic form of glucocorticoid, have increasingly been realized. Considering the fact, the abnormal activation of the NF-κB resulting from severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection might be associated with the pathogenic profile of immune cells, cytokine storm and multiorgan defects. Thus, the pharmacological inactivation of the NF-κB signalling pathway can strongly represent a potential therapeutic target to treat the symptomatology of COVID-19. This article signifies pharmacological blockade of the phosphorylation of inhibitor of nuclear factor kappa B kinase subunit beta (IKKβ), a key downstream effector of NF-κB signalling, for a therapeutic consideration to attenuate COVID-19.
Keywords: COVID-19; IKKβ inhibitors; Inflammation; NF-kB; SARS-CoV-2.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Andreakos E, Sacre SM, Smith C, Lundberg A, Kiriakidis S, Stonehouse T, Monaco C, Feldmann M, Foxwell BM. Distinct pathways of LPS-induced NF-kappa B activation and cytokine production in human myeloid and nonmyeloid cells defined by selective utilization of MyD88 and Mal/TIRAP. Blood. 2004;103:2229–2237. doi: 10.1182/blood-2003-04-1356. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous