Unilateral Exserohilum Allergic Fungal Sinusitis in a Pediatric Host: Case Report
- PMID: 33395877
- PMCID: PMC7711179
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijscr.2020.11.062
Unilateral Exserohilum Allergic Fungal Sinusitis in a Pediatric Host: Case Report
Abstract
Introduction: Allergic fungal sinusitis (AFS) is a result of an inflammatory reaction to fungi in the nasal and paranasal sinuses. Although the causative agents of AFS vary, Exserohilum species are among the rare ones, as only a few cases have ever been reported a few times in the literature. The objective of this report is to highlight this unusual fungal type causing unilateral AFS in Saudi Arabia.
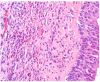
Presentation of the case: We present a case of AFS who initially presented at the age of 15 years, and was operated on in 2015 by another health care provider. He presented again in 2019 complaining of intermittent loss of smell and greenish nasal discharge, mainly from the right side for 3 months, which was associated with right-sided nasal obstruction. Based on the history and physical examination, a diagnosis of refractory chronic rhinosinusitis was made. The patient underwent functional endoscopic sinus surgery (FESS) of the paranasal sinuses and polypectomy. Histopathology of the samples taken during the surgery showed Exserohilum specie. The diagnosis of AFS was confirmed using Bent and Kuhn's criteria.
Discussion: Allergic fungal sinusitis is believed to be an allergic reaction caused by a broad spectrum of species, the majority being Aspergillus in India and Saudi Arabia. Exserohilum species are one of the rare organisms causing AFS in our region.
Conclusion: Most cases of AFS in our region have been reported to be caused by Aspergillus. Here we report a case of unilateral Exserohilum AFS in an immunocompetent pediatric patient.
Keywords: Case report; Exserohilum species; Unilateral allergic fungal sinusitis.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Marglani O. Update in the management of allergic fungal sinusitis. Saudi Med. J. 2014;35(8):791–795. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

