Large leiomyomatosis peritonealis disseminata after laparoscopic myomectomy: A case report with literature review
- PMID: 33395914
- PMCID: PMC7725661
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijscr.2020.12.005
Large leiomyomatosis peritonealis disseminata after laparoscopic myomectomy: A case report with literature review
Abstract
Introduction: Leiomyomatosis peritonealis disseminata (LPD) is a rare disease in which multiple leiomyomas are formed intraperitoneally. Several LPD cases were associated with laparoscopic myomectomy using power morcellators; however, LPD with a large tumor size remains extremely rare. We present a case of large LPD occurring after laparoscopic surgery.
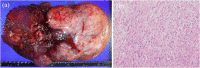
Presentation of case: A 26-year-old woman, gravida 0, underwent laparoscopic myomectomy with power morcellation in our institution. After 5 years, follow-up examination revealed pelvic tumors. Although we recommended resection, she refused and only wanted to be followed up. After 9 years from the first surgery, the tumors became symptomatic and were increasing in number (>10 nodules) and size (>15 cm). Needle biopsy detected leiomyoma. Computed tomography angiography showed that omental and mesenteric arteries were feeding the tumors. We performed laparotomy, and all the 19 tumors emerging from the omentum and mesenterium and weighing 7647 g in total were removed without injuring other organs. The maximum diameter of the largest tumor was 34 cm. The pathological diagnosis was nonmalignant LPD with leiomyoma.
Discussion: Among all reported cases, our case had the largest LPD size. The tumors reached such a huge size because of two possible reasons: (1) they gradually grew asymptomatically over a long period from the time of diagnosis, and (2) they were fed by particularly large vessels, including the omental and mesenteric arteries.
Conclusion: A large LPD is not always symptomatic. After a laparoscopic myomectomy, especially with power morcellation, long-term follow-up is necessary to detect LPD.
Keywords: Case report; Leiomyomatosis peritonealis disseminata; Morcellation; Parasitic myoma.
Copyright © 2020 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Al-Talib A., Tulandi T. Pathophysiology and possible iatrogenic cause of leiomyomatosis peritonealis disseminata. Gynecol. Obstet. Invest. 2010;69:239–244. - PubMed
-
- Willson J.R., Peale A.R. Multiple peritoneal leiomyomas associated with a granulosa-cell tumor of the ovary. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 1952;64:204–208. - PubMed
-
- Li J., Dai S. Leiomyomatosis peritonealis disseminata: a clinical analysis of 13 cases and literature review. Int. J. Surg. Pathol. 2020;28:163–168. - PubMed
-
- Nezhat C., Kho K. Iatrogenic myomas: new class of myomas? J. Minim. Invasive Gynecol. 2010;17:544–550. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

