Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy lesion and brain parenchymal segmentation from MRI using serial deep convolutional neural networks
- PMID: 33395989
- PMCID: PMC7708929
- DOI: 10.1016/j.nicl.2020.102499
Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy lesion and brain parenchymal segmentation from MRI using serial deep convolutional neural networks
Abstract
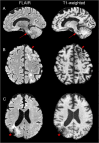
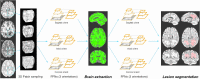
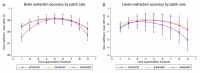
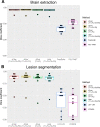
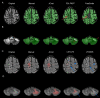
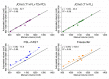
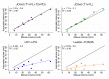
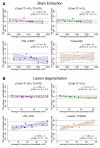
Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML) is a rare opportunistic brain infection caused by the JC virus and associated with substantial morbidity and mortality. Accurate MRI assessment of PML lesion burden and brain parenchymal atrophy is of decisive value in monitoring the disease course and response to therapy. However, there are currently no validated automatic methods for quantification of PML lesion burden or associated parenchymal volume loss. Furthermore, manual brain or lesion delineations can be tedious, require the use of valuable time resources by radiologists or trained experts, and are often subjective. In this work, we introduce JCnet (named after the causative viral agent), an end-to-end, fully automated method for brain parenchymal and lesion segmentation in PML using consecutive 3D patch-based convolutional neural networks. The network architecture consists of multi-view feature pyramid networks with hierarchical residual learning blocks containing embedded batch normalization and nonlinear activation functions. The feature maps across the bottom-up and top-down pathways of the feature pyramids are merged, and an output probability membership generated through convolutional pathways, thus rendering the method fully convolutional. Our results show that this approach outperforms and improves longitudinal consistency compared to conventional, state-of-the-art methods of healthy brain and multiple sclerosis lesion segmentation, utilized here as comparators given the lack of available methods validated for use in PML. The ability to produce robust and accurate automated measures of brain atrophy and lesion segmentation in PML is not only valuable clinically but holds promise toward including standardized quantitative MRI measures in clinical trials of targeted therapies. Code is available at: https://github.com/omarallouz/JCnet.
Keywords: Brain parenchymal fraction; Convolutional neural networks; Deep learning; Lesion segmentation; Magnetic resonance imaging; Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The neuroradiology of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy: a clinical trial perspective.Brain. 2022 Apr 18;145(2):426-440. doi: 10.1093/brain/awab419. Brain. 2022. PMID: 34791056 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DeepNAT: Deep convolutional neural network for segmenting neuroanatomy.Neuroimage. 2018 Apr 15;170:434-445. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2017.02.035. Epub 2017 Feb 20. Neuroimage. 2018. PMID: 28223187 Free PMC article.
-
Association of Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy Lesion Volume With JC Virus Polymerase Chain Reaction Results in Cerebrospinal Fluid of Natalizumab-Treated Patients With Multiple Sclerosis.JAMA Neurol. 2018 Jul 1;75(7):827-833. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2018.0094. JAMA Neurol. 2018. PMID: 29532061 Free PMC article.
-
Fully automated longitudinal segmentation of new or enlarged multiple sclerosis lesions using 3D convolutional neural networks.Neuroimage Clin. 2020;28:102445. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2020.102445. Epub 2020 Sep 24. Neuroimage Clin. 2020. PMID: 33038667 Free PMC article.
-
Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy in patients treated with fumaric acid esters: a review of 19 cases.J Neurol. 2017 Jun;264(6):1155-1164. doi: 10.1007/s00415-017-8509-9. Epub 2017 May 23. J Neurol. 2017. PMID: 28536921 Review.
Cited by
-
A rare case of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy.Radiol Case Rep. 2024 Aug 7;19(10):4654-4658. doi: 10.1016/j.radcr.2024.07.092. eCollection 2024 Oct. Radiol Case Rep. 2024. PMID: 39220789 Free PMC article.
-
FLAMeS: A Robust Deep Learning Model for Automated Multiple Sclerosis Lesion Segmentation.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 May 23:2025.05.19.25327707. doi: 10.1101/2025.05.19.25327707. medRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40475145 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
The neuroradiology of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy: a clinical trial perspective.Brain. 2022 Apr 18;145(2):426-440. doi: 10.1093/brain/awab419. Brain. 2022. PMID: 34791056 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Carson, K.R., Evens, A.M., Richey, E.A., Habermann, T.M., Focosi, D., Seymour, J.F., Laubach, J., Bawn, S.D., Gordon, L.I., Winter, J.N., Furman, R.R., Vose, J.M., Zelenetz, A.D., Mamtani, R., Raisch, D.W., Dorshimer, G.W., Rosen, S.T., Muro, K., Gottardi-Littell, N.R., Talley, R.L., Sartor, O., Green, D., Major, E.O., Bennett, C.L., 2009. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy after rituximab therapy in HIV-negative patients: A report of 57 cases from the Research on Adverse Drug Events and Reports project. Blood 113, 4834–4840. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2008-10-186999. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chollet F. Manning. Manning Publications Co.; Shelter Island NY: 2017. Deep Learning with Python.
-
- Çiçek Ö., Abdulkadir A., Lienkamp S.S., Brox T., Ronneberger O. 3D U-Net: Learning Dense Volumetric Segmentation from Sparse Annotation. Lect. Notes Comput. Sci. (including Subser. Lect. Notes Artif. Intell. Lect. Notes Bioinformatics) 2016;9901 LNCS:424–432.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

