Promoting Human Nutrition and Health through Plant Metabolomics: Current Status and Challenges
- PMID: 33396370
- PMCID: PMC7823625
- DOI: 10.3390/biology10010020
Promoting Human Nutrition and Health through Plant Metabolomics: Current Status and Challenges
Abstract
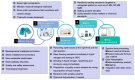
Plant metabolomics plays important roles in both basic and applied studies regarding all aspects of plant development and stress responses. With the improvement of living standards, people need high quality and safe food supplies. Thus, understanding the pathways involved in the biosynthesis of nutritionally and healthily associated metabolites in plants and the responses to plant-derived biohazards in humans is of equal importance to meet people's needs. For each, metabolomics has a vital role to play, which is discussed in detail in this review. In addition, the core elements of plant metabolomics are highlighted, researches on metabolomics-based crop improvement for nutrition and safety are summarized, metabolomics studies on plant natural products including traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) for health promotion are briefly presented. Challenges are discussed and future perspectives of metabolomics as one of the most important tools to promote human nutrition and health are proposed.
Keywords: bioactive compounds; food safety; human health; human nutrition; metabolomics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

