Interferon-α2b Treatment for COVID-19 Is Associated with Improvements in Lung Abnormalities
- PMID: 33396578
- PMCID: PMC7824252
- DOI: 10.3390/v13010044
Interferon-α2b Treatment for COVID-19 Is Associated with Improvements in Lung Abnormalities
Abstract
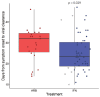
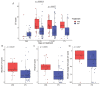
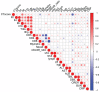
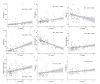
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection causes coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), a lung disease that may progress to systemic organ involvement and in some cases, death. The identification of the earliest predictors of progressive lung disease would allow for therapeutic intervention in those cases. In an earlier clinical study, individuals with moderate COVID-19 were treated with either arbidol (ARB) or inhaled interferon (IFN)-α2b +/-ARB. IFN treatment resulted in accelerated viral clearance from the upper airways and in a reduction in the circulating levels of the inflammatory biomarkers IL-6 and C-reactive protein (CRP). We have extended the analysis of this study cohort to determine whether IFN treatment had a direct effect on virus-induced lung abnormalities and also to ascertain whether any clinical or immune parameters are associated with worsening of lung abnormalities. Evidence is provided that IFN-α2b treatment limits the development of lung abnormalities associated with COVID-19, as assessed by CT images. Clinical predictors associated with worsening of lung abnormalities include low CD8+ T cell numbers, low levels of circulating albumin, high numbers of platelets, and higher levels of circulating interleukin (IL)-10, IL-6, and C-reactive protein (CRP). Notably, in this study cohort, IFN treatment resulted in a higher percentage of CD8+ T cells, lower tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α levels and, as reported earlier, lower IL-6 levels. Independent of treatment, age and circulating levels of albumin and CRP emerged as the strongest predictors of the severity of lung abnormalities.
Keywords: COVID-19; CT images; interferon.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

