Vertical Ridge Augmentation of Fibula Flap in Mandibular Reconstruction: A Comparison between Vertical Distraction, Double-Barrel Flap and Iliac Crest Graft
- PMID: 33396707
- PMCID: PMC7795399
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm10010101
Vertical Ridge Augmentation of Fibula Flap in Mandibular Reconstruction: A Comparison between Vertical Distraction, Double-Barrel Flap and Iliac Crest Graft
Abstract
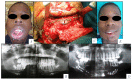
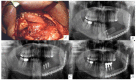
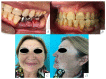
Double-barrel flap, vertical distraction and iliac crest graft are used to reconstruct the vertical height of the fibula. Twenty-four patients with fibula flap were reconstructed comparing these techniques (eight patients in each group) in terms of height of bone, bone resorption, implant success rate and the effects of radiotherapy. The increase in vertical bone with vertical distraction, double-barrel flap and iliac crest was 12.5 ± 0.78 mm, 18.5 ± 0.5 mm, and 17.75 ± 0.6 mm, (p < 0.001). The perimplant bone resorption was 2.31 ± 0.12 mm, 1.23 ± 0.09 mm and 1.43 ± 0.042 mm (p < 0.001), respectively. There were significant differences in vertical bone reconstruction and bone resorption between double-barrel flap and vertical distraction and between iliac crest and vertical distraction (p < 0.001). The study did not show significant differences in implant failure (p = 0.346). Radiotherapy did not affect vertical bone reconstruction (p = 0.125) or bone resorption (p = 0.237) but it showed higher implant failure in radiated patients (p = 0.015). The double-barrel flap and iliac crest graft showed better stability in the height of bone and less bone resorption and higher implant success rates compared with vertical distraction. Radiation therapy did not affect the vertical bone reconstruction but resulted in a higher implant failure.
Keywords: double-barrel flap; fibula flap; iliac crest graft; vertical augmentation; vertical distraction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Melville J.C., Manis C.S., Shum J.W., Alsuwied D. Single-Unit 3D- Printed Titanium reconstruction: The evolution of surgicasl reconstruction for maxillary defects—A case report and review of current techniques. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2019;77:874.e1–874.e13. doi: 10.1016/j.joms.2018.11.030. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Swendseid B., Roden D.F., Vimawala S., Richa T., Sweeny L., Goldman R.A., Luginbuhl A., Heffelfinger R.N., Khanna S., Curry J.M. Virtual Surgical Planning in Subscapular System Free Flap Reconstruction of midface defects. Oral Oncol. 2020;101:104508. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2019.104508. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

