Hydrodechlorination of 4-Chlorophenol on Pd-Fe Catalysts on Mesoporous ZrO2SiO2 Support
- PMID: 33396955
- PMCID: PMC7795707
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules26010141
Hydrodechlorination of 4-Chlorophenol on Pd-Fe Catalysts on Mesoporous ZrO2SiO2 Support
Abstract
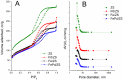
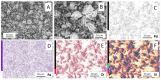
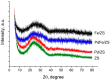
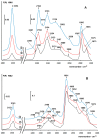
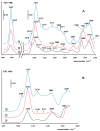
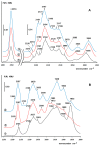
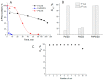
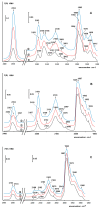
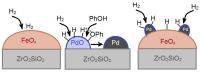
A mesoporous support based on silica and zirconia (ZS) was used to prepare monometallic 1 wt% Pd/ZS, 10 wt% Fe/ZS, and bimetallic FePd/ZS catalysts. The catalysts were characterized by TPR-H2, XRD, SEM-EDS, TEM, AAS, and DRIFT spectroscopy of adsorbed CO after H2 reduction in situ and tested in hydrodechlorination of environmental pollutant 4-chlorophelol in aqueous solution at 30 °C. The bimetallic catalyst demonstrated an excellent activity, selectivity to phenol and stability in 10 consecutive runs. FePd/ZS has exceptional reducibility due to the high dispersion of palladium and strong interaction between FeOx and palladium, confirmed by TPR-H2, DRIFT spectroscopy, XRD, and TEM. Its reduction occurs during short-time treatment with hydrogen in an aqueous solution at RT. The Pd/ZS was more resistant to reduction but can be activated by aqueous phenol solution and H2. The study by DRIFT spectroscopy of CO adsorbed on Pd/ZS reduced in harsh (H2, 330 °C), medium (H2, 200 °C) and mild conditions (H2 + aqueous solution of phenol) helped to identify the reasons of the reducing action of phenol solution. It was found that phenol provided fast transformation of Pd+ to Pd0. Pd/ZS also can serve as an active and stable catalyst for 4-PhCl transformation to phenol after proper reduction.
Keywords: 4-chlorophenol; bimetallic catalyst; hydrodechlorination; iron; mild reduction; palladium; phenol; silica; zirconium oxide.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Lokteva E., Golubina E., Likholobov V., Lunin V. Disposal of Chlorine-Containing Wastes. In: Tundo P., He L.-N., Lokteva E., Mota C., editors. Chemistry Beyond Chlorine. Springer International Publishing; Cham, Switzerland: 2016. pp. 559–584. - DOI
-
- Shi W., Yu N., Jiang X., Han Z., Wang S., Zhang X., Wei S., Giesy J.P., Yu H. Influence of blooms of phytoplankton on concentrations of hydrophobic organic chemicals in sediments and snails in a hyper-eutrophic, freshwater lake. Water Res. 2017;113:22–31. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2017.01.059. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ma J., Hung H., Tian C., Kallenborn R. Revolatilization of persistent organic pollutants in the Arctic induced by climate change. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2011;1:255–260. doi: 10.1038/nclimate1167. - DOI
-
- Yuan G., Keane M.A. Liquid phase catalytic hydrodechlorination of chlorophenols at 273 K. Catal. Commun. 2003;4:195–201. doi: 10.1016/S1566-7367(03)00033-5. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

