2019 novel coronavirus disease with secondary ischemic stroke: two case reports
- PMID: 33397310
- PMCID: PMC7781816
- DOI: 10.1186/s12883-020-02033-3
2019 novel coronavirus disease with secondary ischemic stroke: two case reports
Abstract
Background: The COVID-19 pandemic, which broke out in Wuhan in 2019, has become the global health crisis of our time. Elderly patients with certain fundamental diseases are more likely to develop severe cases. The secondary lesion following viral infection have only rarely been reported.
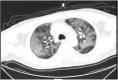
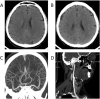
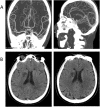
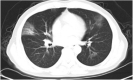
Case presentation: We here report two cases of coronavirus-infected pneumonia with acute ischemic stroke in middle-aged patients. In both COVID-19 cases, neurological physical examinations showed normal results before infection. Lymphocytopenia, accompanied by elevated cytokines and D-dimers, were found from serum clinical laboratory examination at admission. Dysarthria and limb muscle weakness are initial manifestations, occurring one week after infect-causative pathogen, SARS-CoV-2. The head CT and head/neck arterial CTA showed small-vessel occlusion. The patients were diagnosed with coronavirus diseases with secondary acute ischemic stroke. They were treated with tirofiban and followed up with daily aspirin and atorvastatin.
Conclusions: These cases suggested that secondary ischemic stroke, mainly manifested as small-vessel occlusion, should be considered for COVID-19 patients and diagnosed and treated promptly.
Keywords: Coronavirus disease-19 (COVID-19); Secondary ischemic stroke; Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors state that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

