Taking the Myc out of cancer: toward therapeutic strategies to directly inhibit c-Myc
- PMID: 33397405
- PMCID: PMC7780693
- DOI: 10.1186/s12943-020-01291-6
Taking the Myc out of cancer: toward therapeutic strategies to directly inhibit c-Myc
Abstract
c-Myc is a transcription factor that is constitutively and aberrantly expressed in over 70% of human cancers. Its direct inhibition has been shown to trigger rapid tumor regression in mice with only mild and fully reversible side effects, suggesting this to be a viable therapeutic strategy. Here we reassess the challenges of directly targeting c-Myc, evaluate lessons learned from current inhibitors, and explore how future strategies such as miniaturisation of Omomyc and targeting E-box binding could facilitate translation of c-Myc inhibitors into the clinic.
Keywords: Leucine zipper; Oncogene; Peptide; Protein-protein interaction; Transcription.
Conflict of interest statement
JMM is an advisor to Sapience Therapeutics. The authors declare no other competing interests.
Figures
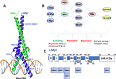
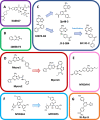
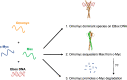
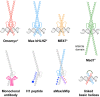
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- BB/T018275/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- A26941/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- MR/T028254/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB/R017956/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- 26941/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

