Cryoelectron-microscopy structure of the enteropathogenic Escherichia coli type III secretion system EspA filament
- PMID: 33397726
- PMCID: PMC7812819
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2022826118
Cryoelectron-microscopy structure of the enteropathogenic Escherichia coli type III secretion system EspA filament
Abstract
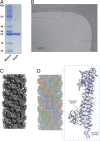
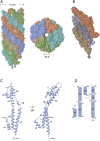
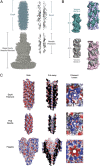
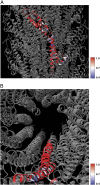
Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli (EPEC) and enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli (EHEC) utilize a macromolecular type III secretion system (T3SS) to inject effector proteins into eukaryotic cells. This apparatus spans the inner and outer bacterial membranes and includes a helical needle protruding into the extracellular space. Thus far observed only in EPEC and EHEC and not found in other pathogenic Gram-negative bacteria that have a T3SS is an additional helical filament made by the EspA protein that forms a long extension to the needle, mediating both attachment to eukaryotic cells and transport of effector proteins through the intestinal mucus layer. Here, we present the structure of the EspA filament from EPEC at 3.4 Å resolution. The structure reveals that the EspA filament is a right-handed 1-start helical assembly with a conserved lumen architecture with respect to the needle to ensure the seamless transport of unfolded cargos en route to the target cell. This functional conservation is despite the fact that there is little apparent overall conservation at the level of sequence or structure with the needle. We also unveil the molecular details of the immunodominant EspA epitope that can now be exploited for the rational design of epitope display systems.
Keywords: attaching/effacing pathogens; bacterial pathogenesis; intestinal epithelium.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures

References
-
- Chen H. D., Frankel G., Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli: Unravelling pathogenesis. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 29, 83–98 (2005). - PubMed
-
- Pennington H., Escherichia coli O157. Lancet 376, 1428–1435 (2010). - PubMed
-
- Deng W., et al. , Assembly, structure, function and regulation of type III secretion systems. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 15, 323–337 (2017). - PubMed
-
- Wilson R. K., Shaw R. K., Daniell S., Knutton S., Frankel G., Role of EscF, a putative needle complex protein, in the type III protein translocation system of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli. Cell. Microbiol. 3, 753–762 (2001). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

