A Cross-Sectional Study of Nemaline Myopathy
- PMID: 33397769
- PMCID: PMC8055318
- DOI: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000011458
A Cross-Sectional Study of Nemaline Myopathy
Abstract
Objective: Nemaline myopathy (NM) is a rare neuromuscular condition with clinical and genetic heterogeneity. To establish disease natural history, we performed a cross-sectional study of NM, complemented by longitudinal assessment and exploration of pilot outcome measures.
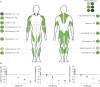
Methods: Fifty-seven individuals with NM were recruited at 2 family workshops, including 16 examined at both time points. Participants were evaluated by clinical history and physical examination. Functional outcome measures included the Motor Function Measure (MFM), pulmonary function tests (PFTs), myometry, goniometry, and bulbar assessments.
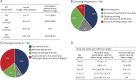
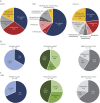
Results: The most common clinical classification was typical congenital (54%), whereas 42% had more severe presentations. Fifty-eight percent of individuals needed mechanical support, with 26% requiring wheelchair, tracheostomy, and feeding tube. The MFM scale was performed in 44 of 57 participants and showed reduced scores in most with little floor/ceiling effect. Of the 27 individuals completing PFTs, abnormal values were observed in 65%. Last, bulbar function was abnormal in all patients examined, as determined with a novel outcome measure. Genotypes included mutations in ACTA1 (18), NEB (20), and TPM2 (2). Seventeen individuals were genetically unresolved. Patients with pathogenic ACTA1 and NEB variants were largely similar in clinical phenotype. Patients without genetic resolution had more severe disease.
Conclusion: We present a comprehensive cross-sectional study of NM. Our data identify significant disabilities and support a relatively stable disease course. We identify a need for further diagnostic investigation for the genetically unresolved group. MFM, PFTs, and the slurp test were identified as promising outcome measures for future clinical trials.
Copyright © 2021 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of the American Academy of Neurology.
Figures


References
-
- Wallgren-Pettersson C, Pelin K, Nowak KJ, et al. . Genotype-phenotype correlations in nemaline myopathy caused by mutations in the genes for nebulin and skeletal muscle alpha-actin. Neuromuscul Disord 2004;14:461–470. - PubMed
-
- Nowak KJ, Wattanasirichaigoon D, Goebel HH, et al. . Mutations in the skeletal muscle alpha-actin gene in patients with actin myopathy and nemaline myopathy. Nat Genet 1999;23:208–212. - PubMed
-
- Agrawal PB, Strickland CD, Midgett C, et al. . Heterogeneity of nemaline myopathy cases with skeletal muscle alpha-actin gene mutations. Ann Neurol 2004;56:86–96. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
