Broadly effective metabolic and immune recovery with C5 inhibition in CHAPLE disease
- PMID: 33398182
- PMCID: PMC7856263
- DOI: 10.1038/s41590-020-00830-z
Broadly effective metabolic and immune recovery with C5 inhibition in CHAPLE disease
Abstract
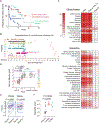
Complement hyperactivation, angiopathic thrombosis and protein-losing enteropathy (CHAPLE disease) is a lethal disease caused by genetic loss of the complement regulatory protein CD55, leading to overactivation of complement and innate immunity together with immunodeficiency due to immunoglobulin wasting in the intestine. We report in vivo human data accumulated using the complement C5 inhibitor eculizumab for the medical treatment of patients with CHAPLE disease. We observed cessation of gastrointestinal pathology together with restoration of normal immunity and metabolism. We found that patients rapidly renormalized immunoglobulin concentrations and other serum proteins as revealed by aptamer profiling, re-established a healthy gut microbiome, discontinued immunoglobulin replacement and other treatments and exhibited catch-up growth. Thus, we show that blockade of C5 by eculizumab effectively re-establishes regulation of the innate immune complement system to substantially reduce the pathophysiological manifestations of CD55 deficiency in humans.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests Statement
The authors M.J.L. and A.O. have a pending patent on C5 inhibitor treatment of CHAPLE. B.S. is a former SomaLogic, Inc. (Boulder, CO, USA) employee and a company shareholder. O.H., Y.G.N., M.D.W., and K.D.N. are employees of Regeneron Pharmaceuticals Inc., a biopharma company. There are no conflicts of interest to report for the remaining coauthors.
Figures




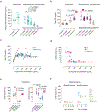

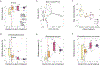
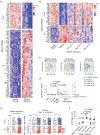
Comment in
-
Complement inhibitor for therapy of CHAPLE.Nat Immunol. 2021 Feb;22(2):106-108. doi: 10.1038/s41590-020-00842-9. Nat Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33398184 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Waldmann TA, Steinfeld JL, Dutcher TF, Davidson JD & Gordon RS Jr. The role of the gastrointestinal system in "idiopathic hypoproteinemia". Gastroenterology 41, 197–207 (1961). - PubMed
-
- Kurolap A et al. Loss of CD55 in Eculizumab-Responsive Protein-Losing Enteropathy. N Engl J Med 377, 87–89 (2017). - PubMed
-
- Ozen A CHAPLE syndrome uncovers the primary role of complement in a familial form of Waldmann's disease. Immunol Rev 287, 20–32 (2019). - PubMed
-
- Mevorach D Clearance of dying cells and systemic lupus erythematosus: the role of C1q and the complement system. Apoptosis 15, 1114–1123 (2010). - PubMed
Methods-only References
-
- Tezcan I, Berkel AI, Ersoy F & Sanal O Sağlıklı Türk çocukları ve erişkinlerde turbidometrik yöntemle bakılan serum immunoglobulin düzeyleri. Çocuk Sağlığı ve Hastalıkları Dergisi 32, 649–656 (1996).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

