Mitochondrial stress induced by continuous stimulation under hypoxia rapidly drives T cell exhaustion
- PMID: 33398183
- PMCID: PMC7971090
- DOI: 10.1038/s41590-020-00834-9
Mitochondrial stress induced by continuous stimulation under hypoxia rapidly drives T cell exhaustion
Abstract
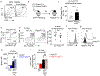
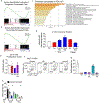
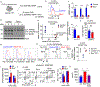
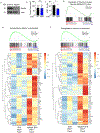
Cancer and chronic infections induce T cell exhaustion, a hypofunctional fate carrying distinct epigenetic, transcriptomic and metabolic characteristics. However, drivers of exhaustion remain poorly understood. As intratumoral exhausted T cells experience severe hypoxia, we hypothesized that metabolic stress alters their responses to other signals, specifically, persistent antigenic stimulation. In vitro, although CD8+ T cells experiencing continuous stimulation or hypoxia alone differentiated into functional effectors, the combination rapidly drove T cell dysfunction consistent with exhaustion. Continuous stimulation promoted Blimp-1-mediated repression of PGC-1α-dependent mitochondrial reprogramming, rendering cells poorly responsive to hypoxia. Loss of mitochondrial function generated intolerable levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS), sufficient to promote exhausted-like states, in part through phosphatase inhibition and the consequent activity of nuclear factor of activated T cells. Reducing T cell-intrinsic ROS and lowering tumor hypoxia limited T cell exhaustion, synergizing with immunotherapy. Thus, immunologic and metabolic signaling are intrinsically linked: through mitigation of metabolic stress, T cell differentiation can be altered to promote more functional cellular fates.
Conflict of interest statement
COMPETING INTERESTS STATEMENT
G.M.D. declares competing financial interests and has submitted patents covering the use of PGC1α in cell therapies that are licensed or pending and is entitled to a share in net income generated from licensing of these patent rights for commercial development. G.M.D. consults for and/or is on the scientific advisory board of BlueSphere Bio, Century Therapeutics, Novasenta, Pieris Pharmaceuticals, and Western Oncolytics/Kalivir; has grants from bluebird bio, Novasenta, Pfizer, Pieris Pharmaceuticals, TCR2, and Western Oncolytics/Kalivir; G.M.D. owns stock in Novasenta.
Figures









Comment in
-
Mitochondria orchestrate T cell fate and function.Nat Immunol. 2021 Mar;22(3):276-278. doi: 10.1038/s41590-020-00861-6. Nat Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33495653 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial dysfunction defines T cell exhaustion.Cell Metab. 2021 Mar 2;33(3):470-472. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2021.02.010. Cell Metab. 2021. PMID: 33657392
-
Reversing the mitochondrial stress-induced exhaustion of CD8+ T cells for improving cancer immunotherapy.Cell Mol Immunol. 2021 Jul;18(7):1634-1637. doi: 10.1038/s41423-021-00709-5. Epub 2021 Jun 7. Cell Mol Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34099891 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

