The effect of Q-switched 1064-nm dymium-doped yttrium aluminum garnet laser on the skin barrier and collagen synthesis through miR-24-3p
- PMID: 33400013
- PMCID: PMC8803697
- DOI: 10.1007/s10103-020-03214-9
The effect of Q-switched 1064-nm dymium-doped yttrium aluminum garnet laser on the skin barrier and collagen synthesis through miR-24-3p
Abstract
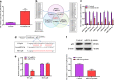
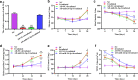
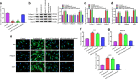
Due to the increase of the world's population aging, how to restore youthfulness to the skin has attracted much attention. It is well known that collagen synthesis and changes in skin barrier play an important role in the process of skin aging. However, whether Q-switched 1064-nm Nd:YAG laser (1064-QSNYL) determines the involvement of miRNAs in skin collagen synthesis and skin barrier changes remains to be elucidated. Upstream miRNAs of p38 molecular pathway have been predicted by bioinformatic database and the relationship between miRNAs and p38 verified by dual-luciferase reporter gene and Western blotting. RT-qPCR analysis detected the expression of miR-24-3p and mRNA for collagen and skin barrier-related molecules, such as keratin 10 (K10), filaggrin, and Aquaporin 4 (APQ4), in mice back skin and in the keratinocyte cell line HaCaT. Western blotting and immunofluorescence (IF) have been used to detect collagen expression and to localize, as well as quantify K10, filaggrin, and APQ4, respectively. In this study, we show that p38 is the main target gene of miRNA-24-3p, and laser irradiation at 1.5 J/cm2 inhibits miR-24-3p expression. Irradiation treatment upregulates the moisture, elasticity, hydroxyproline, and superoxide dismutase content of mice skin, as well as inhibits trans-epidermal water loss. Irradiation also increases collagen, K10, filaggrin, and APQ4 in both mice skin and HaCaT cells. Interestingly, we found that miR-24-3p overexpression inhibits the effect of irradiation on collagen synthesis and skin barrier. We show for the first time that 1064-QSNYL promotes collagen synthesis and protective effects on skin barrier by downregulating miR-24-3p.
Keywords: 1064-nm Q-switched neodymium-doped yttrium aluminum garnet laser; Collagen; Skin barrier; miR-24-3p.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The effect of Q-switched 1064-nm Nd: YAG laser on skin barrier and collagen synthesis via miR-663a to regulate TGFβ1/smad3/p38MAPK pathway.Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 2021 Sep;37(5):412-421. doi: 10.1111/phpp.12673. Epub 2021 Mar 10. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 2021. PMID: 33621359
-
Q-switched 1064-nm dymium-doped yttrium aluminum garnet laser irradiation induces skin collagen synthesis by stimulating MAPKs pathway.Lasers Med Sci. 2019 Jul;34(5):963-971. doi: 10.1007/s10103-018-2683-6. Epub 2018 Nov 17. Lasers Med Sci. 2019. PMID: 30448939
-
Q-Switched 1064 nm Nd:YAG Laser Rejuvenates Photoaging Skin of Rats by Downregulating miR-196b-5p.Photobiomodul Photomed Laser Surg. 2022 Oct;40(10):708-714. doi: 10.1089/photob.2022.0036. Photobiomodul Photomed Laser Surg. 2022. PMID: 36286575
-
Q-switched 1064 nm Nd: YAG laser restores skin photoageing by activating autophagy by TGFβ1 and ITGB1.Exp Dermatol. 2024 Jan;33(1):e15006. doi: 10.1111/exd.15006. Exp Dermatol. 2024. PMID: 38284200
-
Q-switched 1064 nm Nd-Yag nanosecond laser effects on skin barrier function and on molecular rejuvenation markers in keratinocyte-fibroblasts interaction.Lasers Med Sci. 2019 Apr;34(3):595-605. doi: 10.1007/s10103-018-2635-1. Epub 2018 Oct 1. Lasers Med Sci. 2019. PMID: 30276490
Cited by
-
Exploring the therapeutic mechanisms of heart failure with Chinese herbal medicine: a focus on miRNA-mediated regulation.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Nov 5;15:1475975. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1475975. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39564110 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pilot Study to Demonstrate Improvement in Skin Tone and Texture by Treatment with a 1064 nm Q-Switched Neodymium-Doped Yttrium Aluminum Garnet Laser.J Clin Med. 2024 Feb 28;13(5):1380. doi: 10.3390/jcm13051380. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 38592205 Free PMC article.
-
Recent advances in exosomal non-coding RNA-based therapeutic approaches for photoaging.Skin Res Technol. 2023 Sep;29(9):e13463. doi: 10.1111/srt.13463. Skin Res Technol. 2023. PMID: 37753673 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA-24 therapeutic potentials in infarction, stroke, and diabetic complications.Mol Biol Rep. 2024 Nov 9;51(1):1137. doi: 10.1007/s11033-024-10089-4. Mol Biol Rep. 2024. PMID: 39520600 Review.
-
lncRNA NONRATT013819.2 promotes transforming growth factor-β1-induced myofibroblastic transition of hepatic stellate cells by miR24-3p/lox.Open Med (Wars). 2022 Apr 4;17(1):661-675. doi: 10.1515/med-2022-0460. eCollection 2022. Open Med (Wars). 2022. PMID: 35434372 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

