Pulsatile contractions promote apoptotic cell extrusion in epithelial tissues
- PMID: 33400921
- PMCID: PMC7987746
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cub.2020.12.005
Pulsatile contractions promote apoptotic cell extrusion in epithelial tissues
Abstract
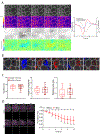
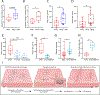
Extrusion is a mechanism used to eliminate unfit, excess, or dying cells from epithelial tissues. The initial events guiding which cells will be selectively extruded from the epithelium are not well understood. Here, we induced damage in a subset of epithelial cells in the developing zebrafish and used time-lapse imaging to examine cell and cytoskeletal dynamics leading to extrusion. We show that cell extrusion is preceded by actomyosin contractions that are pulsatile. Our data show that pulsatile contractions are induced by a junctional to medial re-localization of myosin. Analysis of cell area during contractions revealed that cells pulsing with the longest duration and highest amplitude undergo progressive area loss and extrude. Although pulses were driven by local increases in tension, damage to many cells promoted an overall decrease in the tensile state of the epithelium. We demonstrate that caspase activation leads to sphingosine-1-phosphate enrichment that controls both tissue tension and pulses to dictate areas of extrusion. These data suggest that the kinetics of pulsatile contractions define a key behavioral difference between extruding and non-extruding cells and are predictive of extrusion. Altogether, our study provides mechanistic insight into how localized changes in physical forces are coordinated to remove defective cells for homeostatic maintenance of living epithelial tissues.
Keywords: cell extrusion; epithelia; physical forces; tissue homeostasis; zebrafish.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Rosenblatt J, Raff MC, Cramer LP. An epithelial cell destined for apoptosis signals its neighbors to extrude it by an actin- and myosin-dependent mechanism. Curr Biol. 2001;11(23):1847–57. - PubMed
-
- Hogan C, Dupre-Crochet S, Norman M, Kajita M, Zimmermann C, Pelling AE, et al. Characterization of the interface between normal and transformed epithelial cells. Nat Cell Biol. 2009;11(4):460–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

