AhaP, A Quorum Quenching Acylase from Psychrobacter sp. M9-54-1 That Attenuates Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Vibrio coralliilyticus Virulence
- PMID: 33401388
- PMCID: PMC7823738
- DOI: 10.3390/md19010016
AhaP, A Quorum Quenching Acylase from Psychrobacter sp. M9-54-1 That Attenuates Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Vibrio coralliilyticus Virulence
Abstract
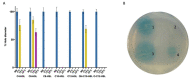
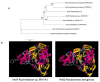
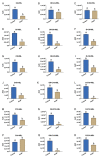
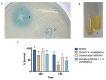
Although Psychrobacter strain M9-54-1 had been previously isolated from the microbiota of holothurians and shown to degrade quorum sensing (QS) signal molecules C6 and C10-homoserine lactone (HSL), little was known about the gene responsible for this activity. In this study, we determined the whole genome sequence of this strain and found that the full 16S rRNA sequence shares 99.78-99.66% identity with Psychrobacter pulmonis CECT 5989T and P. faecalis ISO-46T. M9-54-1, evaluated using the agar well diffusion assay method, showed high quorum quenching (QQ) activity against a wide range of synthetic N-acylhomoserine lactone (AHLs) at 4, 15, and 28 °C. High-performance liquid chromatography-mass-spectrometry (HPLC-MS) confirmed that QQ activity was due to an AHL-acylase. The gene encoding for QQ activity in strain M9-54-1 was identified from its genome sequence whose gene product was named AhaP. Purified AhaP degraded substituted and unsubstituted AHLs from C4- to C14-HSL. Furthermore, heterologous expression of ahaP in the opportunistic pathogen Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 reduced the expression of the QS-controlled gene lecA, encoding for a cytotoxic galactophilic lectin and swarming motility protein. Strain M9-54-1 also reduced brine shrimp mortality caused by Vibrio coralliilyticus VibC-Oc-193, showing potential as a biocontrol agent in aquaculture.
Keywords: Psychrobacter; acylase; marine habitat; quorum quenching.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
- AGL2015-68806-R/Spanish Ministry of the Economy and Competitiveness
- PID2019-106704RB-100/SRA/Spanish Ministry of the Economy and Competitiveness and State Research Agency (AEI)
- FPU15/01717/Spanish Ministry of Education, Culture and Sport
- BB/R012415/1/nnovation and Knowledge Centre funded by the Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council, InnovateUK and Hartree Centre
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

