Crucial Role of FABP3 in αSyn-Induced Reduction of Septal GABAergic Neurons and Cognitive Decline in Mice
- PMID: 33401521
- PMCID: PMC7795765
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22010400
Crucial Role of FABP3 in αSyn-Induced Reduction of Septal GABAergic Neurons and Cognitive Decline in Mice
Abstract
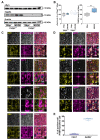
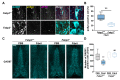
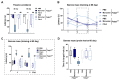
In synucleinopathies, while motor symptoms are thought to be attributed to the accumulation of misfolded α-synuclein (αSyn) in nigral dopaminergic neurons, it remains to be elucidated how cognitive decline arises. Here, we investigated the effects of distinct αSyn strains on cognition and the related neuropathology in the medial septum/diagonal band (MS/DB), a key region for cognitive processing. Bilateral injection of αSyn fibrils into the dorsal striatum potently impaired cognition in mice. The cognitive decline was accompanied by accumulation of phosphorylated αSyn at Ser129 and reduction of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA)-ergic but not cholinergic neurons in the MS/DB. Since we have demonstrated that fatty acid-binding protein 3 (FABP3) is critical for αSyn neurotoxicity in nigral dopaminergic neurons, we investigated whether FABP3 also participates in αSyn pathology in the MS/DB and cognitive decline. FABP3 was highly expressed in GABAergic but rarely in cholinergic neurons in the MS/DB. Notably, Fabp3 deletion antagonized the accumulation of phosphorylated αSyn, decrease in GABAergic neurons, and cognitive impairment caused by αSyn fibrils. Overall, the present study indicates that FABP3 mediates αSyn neurotoxicity in septal GABAergic neurons and the resultant cognitive impairment, and that FABP3 in this subpopulation could be a therapeutic target for dementia in synucleinopathies.
Keywords: cognition; fatty acid-binding protein; gamma-aminobutyric acid; medial septum; α-synuclein.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
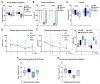
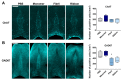
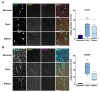
Similar articles
-
Suppression of α-synuclein propagation after intrastriatal injection in FABP3 null mice.Brain Res. 2021 Jun 1;1760:147383. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2021.147383. Epub 2021 Feb 24. Brain Res. 2021. PMID: 33636166
-
Development of FABP3 ligands that inhibit arachidonic acid-induced α-synuclein oligomerization.Brain Res. 2019 Mar 15;1707:190-197. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2018.11.036. Epub 2018 Nov 26. Brain Res. 2019. PMID: 30496735
-
Fatty Acid-Binding Protein 3 is Critical for α-Synuclein Uptake and MPP+-Induced Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Cultured Dopaminergic Neurons.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Oct 28;20(21):5358. doi: 10.3390/ijms20215358. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31661838 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of fatty acid-binding proteins and dopamine receptors on α-synucleinopathy.J Pharmacol Sci. 2022 Feb;148(2):248-254. doi: 10.1016/j.jphs.2021.12.003. Epub 2021 Dec 14. J Pharmacol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35063140 Review.
-
alpha-Synucleinopathy models and human neuropathology: similarities and differences.Acta Neuropathol. 2008 Jan;115(1):87-95. doi: 10.1007/s00401-007-0302-x. Epub 2007 Oct 12. Acta Neuropathol. 2008. PMID: 17932682 Review.
Cited by
-
Cognitive dysfunction in animal models of human lewy-body dementia.Front Aging Neurosci. 2024 Jul 22;16:1369733. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2024.1369733. eCollection 2024. Front Aging Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39104707 Free PMC article. Review.
-
α-Synuclein reduces acetylserotonin O-methyltransferase mediated melatonin biosynthesis by microtubule-associated protein 1 light chain 3 beta-related degradation pathway.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024 Jan 27;81(1):61. doi: 10.1007/s00018-023-05053-7. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024. PMID: 38279053 Free PMC article.
-
Heart fatty acid-binding protein is associated with phosphorylated tau and longitudinal cognitive changes.Front Aging Neurosci. 2022 Oct 10;14:1008780. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2022.1008780. eCollection 2022. Front Aging Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36299612 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

