Inhibitory Effect of Nepeta deflersiana on Climax Bacterial Community Isolated from the Oral Plaque of Patients with Periodontal Disease
- PMID: 33401536
- PMCID: PMC7795411
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules26010202
Inhibitory Effect of Nepeta deflersiana on Climax Bacterial Community Isolated from the Oral Plaque of Patients with Periodontal Disease
Abstract
Background: The red-complex bacteria are one of the most significant complexes found simultaneously in subgingival plaque next to the periodontal pocket. The current antibacterial treatment is not adequate, and multidrug resistance to it is developing. Henceforth, the antibacterial effect of the ethanolic extract of Nepeta deflersiana was put to test against red-complex bacteria in patients with chronic periodontitis.
Methods: Well diffusion and micro broth dilution procedure by Alamar blue were applied to assess the zone of inhibition (ZOI), the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC), and the minimum bactericidal concentration (MBC). Anti-virulence efficacies of the plant extract that comprise of adherence and formation of biofilms were examined by the process of adherence and biofilm production assay.
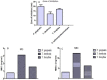
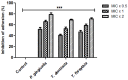
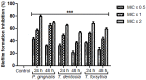
Results: The crude extract of Nepeta deflersiana exhibited significant inhibitory outcome against periodontopathic bacteria with noteworthy MIC (0.78-3.12 mg/mL), inhibitory zone (12-20 mm), as well as MBC (3.12-12.50 mg/mL). The N. deflersiana extract inhibited bacterial adhesion ranging from 41% to 52%, 53% to 66%, and 60% to 79% at the given MIC × 0.5, MIC × 1, and MIC × 2 in succession. Substantial suppression was also developed in the biofilm production of the investigated periodontopathic strains following exposure to numerous concentrations of N. deflersianan extract for a period of 24 and 48 h.
Conclusion: These outcomes divulge a new concept that N. deflersiana extract can be utilized to manufacture valuable antibacterial compounds to treat chronic and acute periodontitis. This identifies N. deflersiana as an essential natural source for future drug development.
Keywords: N. deflersiana; antibacterial activity; biofilm; periodontal disease; red-complex bacteria.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Nayak A., Bhat K., Shivanaikar S., Pushpa P., Kugaji M., Kumbar V. Detection of red complex organisms in chronic periodontitis by multiplex polymerase chain reaction. J. Adv. Clin. Res. Insights. 2018;5:139–144. doi: 10.15713/ins.jcri.231. - DOI
-
- Mahalakshmi K., Krishnan P., Chandrasekaran S.C., Panishankar K.H., Subashini N. Prevalence of periodontopathic bacteria in the south subgingival plaque of a South Indian population with periodontitis. J. Clin. Diag. Res. 2012;6:747–752.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

