Natural Food Supplements Reduce Oxidative Stress in Primary Neurons and in the Mouse Brain, Suggesting Applications in the Prevention of Neurodegenerative Diseases
- PMID: 33401699
- PMCID: PMC7824423
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox10010046
Natural Food Supplements Reduce Oxidative Stress in Primary Neurons and in the Mouse Brain, Suggesting Applications in the Prevention of Neurodegenerative Diseases
Abstract
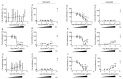
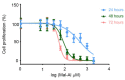
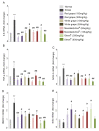
Neurodegenerative diseases pose a major health problem for developed countries, and stress has been identified as one of the main risk factors in the development of these disorders. Here, we have examined the protective properties against oxidative stress of several bioactive natural food supplements. We found that MecobalActive®, Olews®, and red and white grape seed polyphenol extracts may have a neuroprotective effect in vitro, both in the SH-SY 5Y cell line and in hippocampal neuron cultures, mainly by reducing reactive oxygen species levels and decreasing caspase-3 activity. In vivo, we demonstrated that oral administration of the supplements reduces the expression of genes involved in inflammation and oxidation mechanisms, whereas it increments the expression of genes related to protection against oxidative stress. Furthermore, we found that preventive treatment with these natural extracts increases the activity of antioxidant enzymes and prevents lipid peroxidation in the brain of stressed mice. Thus, our results indicate that some natural bioactive supplements may have important protective properties against oxidative stress processes occurring in the brain.
Keywords: MecobalActive®; Olews®; ROS; neurodegenerative diseases; oxidative stress; red grape polyphenol extract; white grape seed polyphenol extract.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures




References
-
- Litvan I., Goldman J.G., Troster A.I., Schmand B.A., Weintraub D., Petersen R.C., Mollenhauer B., Adler C.H., Marder K., Williams-Gray C.H., et al. Diagnostic criteria for mild cognitive impairment in Parkinson’s disease: Movement Disorder Society Task Force guidelines. Mov. Disord. 2012;27:349–356. doi: 10.1002/mds.24893. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Choi H.I., Lee H.W., Eom T.M., Lim S.A., Ha H.Y., Seol I.C., Kim Y.S., Oh D.S., Yoo H.R. A traditional Korean multiple herbal formulae (Yuk-Mi-Jihwang-Tang) attenuates acute restraint stress-induced brain tissue oxidation. Drug Chem. Toxicol. 2017;40:125–133. doi: 10.1080/01480545.2016.1183209. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

