The Association between Dynamic Changes in Serum Presepsin Levels and Mortality in Immunocompromised Patients with Sepsis: A Prospective Cohort Study
- PMID: 33401701
- PMCID: PMC7823693
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics11010060
The Association between Dynamic Changes in Serum Presepsin Levels and Mortality in Immunocompromised Patients with Sepsis: A Prospective Cohort Study
Abstract
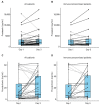
Presepsin is a subtype of soluble CD14 that is increased in the blood of septic patients. We investigated the role of dynamic changes in serum presepsin levels in critically ill, immunocompromised patients with sepsis. This is a prospective cohort study that included 119 adult patients admitted to the intensive care unit (ICU). Presepsin level was measured on day 1 and day 3 after ICU admission. The primary outcome was in-hospital mortality. In immunocompromised patients, presepsin levels on day 1 were higher in patients with sepsis than those in patients without sepsis. The area under the curve (AUC) of presepsin for diagnosing sepsis in immunocompromised patients was 0.87, which was comparable with that of procalcitonin (AUC, 0.892). Presepsin levels on day 3 were higher in patients who died in the hospital than in those who survived. In immunocompromised patients who died in the hospital, presepsin levels on day 3 were significantly higher than those on day 1. In the multivariate analysis, ΔPresepsin+ alone was independently correlated with in-hospital mortality in immunocompromised patients. These findings suggest that dynamic changes in presepsin levels between day 1 and day 3 are associated with in-hospital mortality in patients with sepsis, especially in immunocompromised patients.
Keywords: immunocompromised; presepsin; sepsis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Singer M., Deutschman C.S., Seymour C.W., Shankar-Hari M., Annane D., Bauer M., Bellomo R., Bernard G.R., Chiche J.D., Coopersmith C.M., et al. The Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock (Sepsis-3) JAMA. 2016;315:801–810. doi: 10.1001/jama.2016.0287. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Shozushima T., Takahashi G., Matsumoto N., Kojika M., Okamura Y., Endo S. Usefulness of presepsin (sCD14-ST) measurements as a marker for the diagnosis and severity of sepsis that satisfied diagnostic criteria of systemic inflammatory response syndrome. J. Infect. Chemother. 2011;17:764–769. doi: 10.1007/s10156-011-0254-x. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kirkland T.N., Viriyakosol S. Structure-function analysis of soluble and membrane-bound CD14. Prog. Clin. Biol. Res. 1998;397:79–87. - PubMed
-
- Camussi G., Mariano F., Biancone L., De Martino A., Bussolati B., Montrucchio G., Tobias P.S. Lipopolysaccharide binding protein and CD14 modulate the synthesis of platelet-activating factor by human monocytes and mesangial and endothelial cells stimulated with lipopolysaccharide. J. Immunol. 1995;155:316–324. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

